This site uses cookies. By continuing to browse the site you are agreeing to our use of cookies. Read our privacy policy>
![]()
This site uses cookies. By continuing to browse the site you are agreeing to our use of cookies. Read our privacy policy>
![]()
Enterprise products, solutions & services
Horizon is Huawei’s new digital platform and an integral part of our vision to build a foundation and core for the digital world, in turn supporting the development and digital transformation of customers’ businesses through collaboration with partners.
To achieve this goal, we launched ROMA, a unified data integration platform that forms the basis of the Horizon Digital Platform. ROMA implements extensive connections, integrates the data of different systems, and eliminates siloed structures on customers’ live networks, allowing all data to be shared and applied.
A major aspect of the Horizon Digital Platform and ROMA is system integration. In the IT industry, this means integrating separated systems, data, and other elements into associated, unified, and coordinated systems through various integration methods, including technical, function, data, mode, and business integration. In this way, resources can be fully shared and managed in a centralized, efficient, and convenient way, helping to create more applications.
The key to system integration is handling interconnection and interoperability issues between systems. Indeed, system integration inevitably involves multiple vendors, protocols, and applications.
With traditional integration solutions, developers need to search for various database drivers and build a system step-by-step, based on an open-source protocol framework and the Software Development Kits (SDKs) provided by vendors. Elements such as system robustness, stability, and scalability must all be taken into consideration and such traditional integration solutions pose extremely strict requirements on the comprehensive competence of technical personnel.
According to leading research company Gartner, integration work will account for 60% of the time spent and 60% of the costs incurred, building a digital platform. Yet traditional integration is far too time-consuming and labor-intensive, and cannot meet the business requirements of the digital transformation era.
Integration in the digital era differs from traditional integration in the following ways:
Different users: Traditionally, integration is largely implemented by IT professionals only. However, integration in the digital era is accompanied by more application innovation and requires a lower threshold, so business staff can also implement integration, as well as IT professionals.
Connecting to a wider range of endpoints: In addition to traditional on-premises devices, public clouds, mobile terminals, and IoT devices now also need to be connected.
More integration scenarios: Integration in the digital era includes integration between applications and databases, B2B integration, process integration, multi-cloud integration, and integration based on AI and robot automation. Therefore, many more protocols and databases are involved.
Resource convergence platform: To improve efficiency and the experience, as well as lower costs, developers need to continuously innovate applications. More importantly, enterprises need to collect a wide range of data and build bridges between businesses to create a platform for resource convergence and management, enabling effective resource control.
Higher security level: Data has become a core asset for enterprises. In the digital era, integration must be implemented across departments, organizations, companies, and clouds, posing higher security requirements.
Ease of use: In the digital era, products with increased efficiency are available, lowering learning costs, reducing technical barriers, and supporting quick business transformation and rollout.
Gartner predicts that 65% of large-scale enterprises and global organizations will have turned to a hybrid integration platform by 2022 in order to fulfill their integration requirements.
Standing for for Relationship, Open, Multi-cloud, and Any-connect, ROMA was launched as a basis for integration. It is a hybrid integration platform derived from Huawei’s native applications, drawing on over a decade of Huawei’s digital transformation practices. Equipped with multiple industry suites provided by Huawei and ecosystem partners, as well as more than 20 heterogeneous data sources, it attempts to streamline multiple integration modes, such as the integration of data, messages, APIs, and devices, facilitating integration across networks, domains, and clouds.
Our aim is to make ROMA integral to integration, by making integration easier through it. Critical to this goal are ROMA’s functional components and core architecture.

Our aim is to make ROMA integral to integration, by making integration easier through it. Critical to this goal are ROMA’s functional components and core architecture.
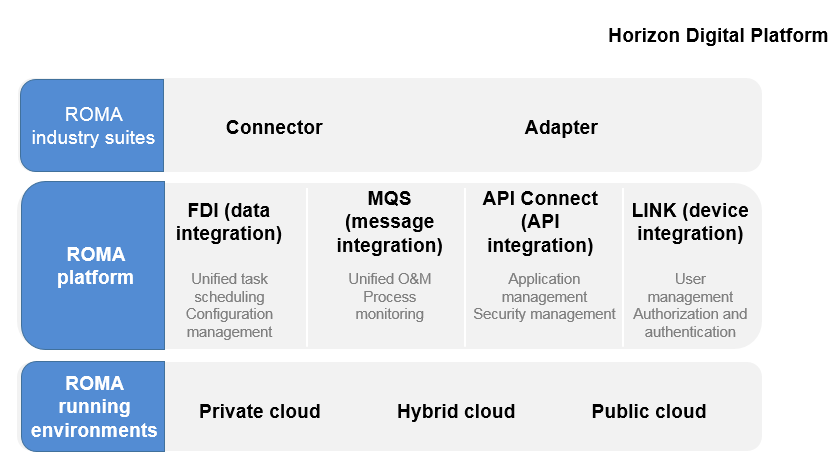
ROMA running environments: ROMA can run independently in private, public, and hybrid cloud environments, without dependency on the underlying hardware.
ROMA platform: FDI (data integration), MQS (message integration), API Connect (service integration), and LINK (device integration) mutually collaborate in order to implement comprehensive connections.
ROMA industry suites: High-quality assets such as system interconnection scripts and configurations developed on the ROMA platform are accumulated as industry suites, including connectors for different southbound protocols and adapters for northbound applications.
Feature 1: Full data aggregation
The data integration component, FDI, is equipped with more than 20 heterogeneous data sources. This means that ROMA can handle data from traditional databases (such as MySQL, Oracle, and SQL Server), big data systems (such as HDFS, Hive, and HBase), and message queuing systems (including Kafka, MQS, and AMQP), as well as data transferred through network protocols such as FTP and RESTful, and device data connected through IoT protocols such as MQTT and COAP.
How does ROMA deal with private protocols?
ROMA opens a protocol customization framework, allowing developers to compile protocol plug-ins, while scheduling and Operations and Maintenance (O&M) are implemented by ROMA. This means that developers no longer need to search for various database drivers and protocol frameworks, or perform task scheduling and system monitoring. All of these functions can now be implemented by ROMA.
More importantly, UI-based configuration is available for all integration work: even if you’re unfamiliar with coding, you can implement integration.
Feature 2: easy application integration
The integration process is comprised of data source configuration, integration task creation, and scheduling policy definition, with each phase configured on the UI. In the past, the process took several days — with ROMA, it takes minutes. Indeed, ROMA makes integration simpler than ever before and there is no need to seek help from IT personnel.

Feature 3: Comprehensive tool collaboration
Besides packets of common databases, simple APIs, and messages, more complex and irregular data cannot be handled by most tools. This is where ROMA stands out and it can, for example, effectively deal with attribute data reported by IoT devices. Indeed, through seamless collaboration among API Connect, MQS, and FDI components, ROMA can even handle complex packets with only a few lines of JavaScript conversion code, and all that is required is configuration-based integration.
In this process, there is no need to consider protocol implementation details, open-source frameworks, or compilation, and programs can run immediately after being developed, minimizing development difficulties. This is ROMA’s low-code development mode — simple, flexible, and powerful.
Feature 4: Integration across networks, domains, and clouds
Many scenarios require cross-network integration of data, messages, and services — including integration between enterprise groups and their branches, education bureaus and schools, chemical park management committees and factories, urban big data bureaus and government agencies, private clouds and public clouds, and between public clouds. ROMA stands out from other industry platforms because it is able to satisfy diverse integration requirements and ensure data security, while offering convenient use of applications.
The overarching purpose of ROMA is to build a resource aggregation platform, contribute to application innovation, and help industries cope with rapid changes in the era of digital transformation. And this is what we continue to strive toward.