This site uses cookies. By continuing to browse the site you are agreeing to our use of cookies. Read our privacy policy>
![]()
This site uses cookies. By continuing to browse the site you are agreeing to our use of cookies. Read our privacy policy>
![]()
Enterprise products, solutions & services
Networks in the healthcare sector need to deal with some specific and demanding requirements. Patient treatment, safety, and comfort should be prioritized at all times. This means that networks will need to deliver future-proof and reliable connectivity so that healthcare staff can focus on giving patients the best care possible. This blog focuses on how fiber to the office (FTTO) can provide a quality network solution for health sector deployments.
The bandwidth requirements for networks in hospitals can be high, and having a future-proof and high-capacity FTTO network matches these needs. For example, medical imaging can produce large amounts of data, which means high-bandwidth networks are a must. With traditional copper-based LAN networks, high network latency means it could take 30 seconds to read 1,000 medical images. However, with FTTO this can be drastically reduced to less than 1 second.
Hospitals also require high-capacity networks since they are large institutions with many employees and patients who, for example, may be using public Wi-Fi networks within the hospital. This is a typical high-concurrency scenario in which more bandwidth will be required. Moreover, there will also be a need for medical devices such as X-ray machinesto be directly connected with fiber in order to guarantee more stable and ultra-high bandwidth.
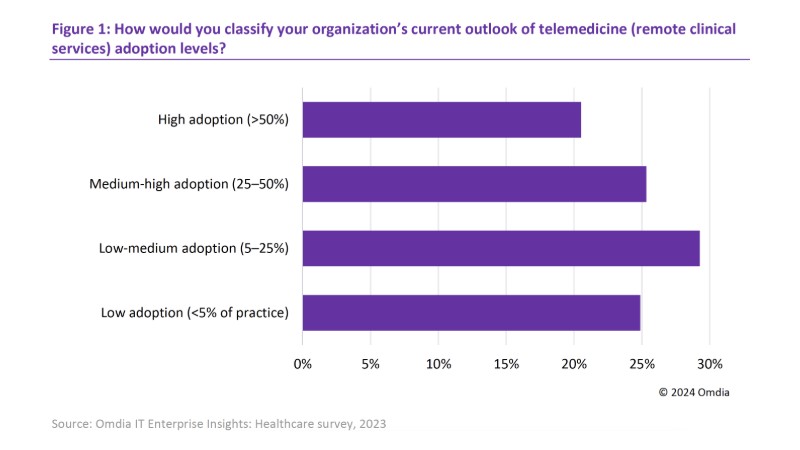
In addition, across different types of healthcare environments telemedicine is being used, for instance, to perform patient consultations remotely. This could involve HD videoconferencing, which increases bandwidth requirements. As part of Omdia’s IT Enterprise Insights: Healthcare survey, respondents across all kinds of healthcare establishments were asked about their organization’s use of telemedicine in 2023,and the responses indicate that usage is already common (see Figure 1). Furthermore, usage will only grow over time, and in the same survey 61% of respondents said their usage of telemedicine would be at or above 25% of their practice in 2028.
Networks in hospitals need to be easy and simple to operate so patient treatment can always be the focus. FTTO can meet this requirement for simplicity because it allows multiple applications to be run over a single optical network. For example, in hospitals connectivity will be needed for a wide variety of applications such as digital signage, connecting medical devices, security cameras in public areas of the hospital, and digital ward-calling systems. The FTTO deployment in the Shenzhen Union Hospital supports an Internet of Things network within the hospital that provides high-quality information sharing for clinics, wards, CT imaging,and other scenarios. A further important benefit of FTTO in this context is that it supports hard slicing whereby different applications can run independently without interfering with each other.
FTTO can also offer simplicity benefits because traditional copper-based LAN networks require many additional equipment rooms because such networks can only provide their maximum bandwidth up to a distance of 100m. FTTO deployments can avoid this additional challenge. This distance limitation for traditional copper-based LAN networks is likely to be particularly problematic in hospitals because the manyareas, such as patient wards and waiting areas, that the network needs to connect are likely to be spread out across the whole hospital building.
A further reason why FTTO networks can deliver greater simplicity is that they require less cabling than traditional copper-based networks. As a result there are fewer points of failure than for traditional copper-based LAN networks, which require much more cabling because they can only provide their maximum speed up to distances of 100m. The greater volume of cabling for copper-based LAN networks also makes such architectures much more complex, and it is more challenging to find the location of faults.
One important benefit of FTTO is that it is a future-proof solution that can offer longer-term savings in total cost of ownership. Bandwidth requirements today are high, and they may also increase further in the future. FTTO is well placed to cost-effectively meet this increase in bandwidth because such networks can be upgraded to 10G PON and even 50G PON without the need to replace cables. Thelifetime of fiber cables is around 30 years. However, traditional copper-based LAN networks need recabling as bandwidths increase, and this could be extremely costly and complex for hospital deployments. For example, the Wuhan Union Hospital, which has deployed an FTTO network, has a proton therapy center for cancer treatment. Because of the radiation from the treatment, network cables need to be buried within very thick concrete, but if a traditional copper-based LAN had been deployed it would then have been very difficult to replace this cabling to accommodate the new treatment. Proton therapy for cancer treatment remains very new, but over time it is likely to be adopted by more hospitals, and hospital staff need to plan hospital network construction in advance.
More generally, recabling work is inappropriate for hospital locations because the construction work can produce dust that could be an irritant to patients and employees and potentially could disrupt sensitive medical equipment. This problem is further compounded if copper-based LAN networks are widely deployed in the hospital. More specifically, networks in hospitals will cover more types of facilities, including rooms for treatment, offices, conferences, and wards, so any recabling work is likely to be needed across the hospital as a whole, leading to substantial costs and disruption to patients.
A further cost-saving benefit of FTTO is that network operations can be centralized, which reduces operating costs and means that any new OLTs and ONUs can be online without delay in case any of these devices needs to be replaced. FTTO networks can be managed from a unified platform and can support intelligent operation and maintenance and network visualization, which means fault detection can easily be implemented. This helps to ensure hospital networks provide high reliability, minimizing disruption to patient care. Another example of an FTTO network providing high network reliability is the Guizhou Provincial People’s Hospital. In this example, high reliability is provided because the network supports full-link protection, dual-homing redundancy, and rapid switchover within 50ms.
Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the official policy, position, products, and technologies of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. If you need to learn more about the products and technologies of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd., please visit our website at e.huawei.com or contact us.