ผลิตภัณฑ์ โซลูชั่น และบริการสำหรับองค์กรธุรกิจ
The world is consuming increasingly more energy, which leads to higher carbon emissions. China's emissions account for a third of the world's total, so a lot rides on the country's contribution to global carbon neutrality goals. On the long journey towards zero carbon, energy transformation will be crucial.
Currently, the global energy and industry systems are undergoing a full-scale energy transformation, looking to reduce carbon emissions and increase the proportion of clean energy. There is a big push to move towards decarbonization, energy systems are evolving to more diversity, and intelligence is playing a larger role in energy optimization.
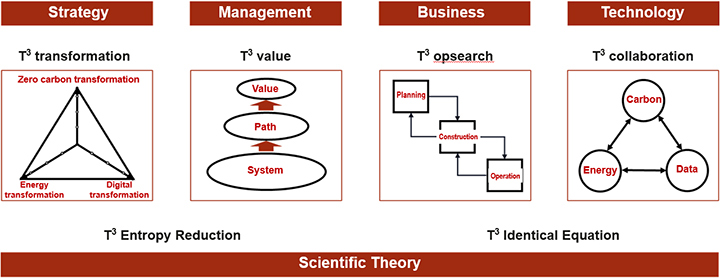
T3 Development System
While energy and information help society advance, they also put a lot of pressure on our environment. The T3 development system proposes a series of methodologies to reverse the negative impact social development has on the environment, and instead, make them work to social benefit. For this, the approach systematically helps reduce energy consumption and carbon emissions at every step of the way, covering strategy, management, business, and technology.
More specifically, the T3 development system refers to the zero carbon, energy, and digital transformations in the ecology, industry, and technology fields, supporting their evolution and upgrade. The model establishes zero-carbon smart energy system centered on data by integrating energy, carbon, information, and value flows. This promotes clean, efficient, and sustainable social development by relying on digital transformation to boost energy transition and approach carbon neutrality targets.
The zero-carbon energy system is a vision for future development. It will be one of the main forces behind achieving global climate targets, safeguarding world energy security, and promoting economic growth. The system focuses on reliability, efficiency, and zero-carbon intelligence. It relies on multi-energy complementary supply, low-carbon energy consumption, and a management and operation system with multi-energy synergy.

T3 Transformation Model for Global Strategic Development
On the national level, we need T3 transformation to help us build integrated zero-carbon smart energy infrastructure powered by digital technologies. For this, we need clear transformation goals based on the current state of national energy, resources, and industries. Policies must guide low-carbon economic development and promote industry upgrade, regional development, energy transition, low-carbon living, energy saving, and environmental protection.
On a municipal level, we should develop capabilities related to zero-carbon and energy transformation, feeding into the larger objectives of T3 transformation. We should rely on digital technologies to enable low-carbon governance, energy efficiency improvement, and carbon-energy synergy, creating a zero-carbon city governance system with integrated planning, construction, and operation.
Within this context, campuses will act as the basic units of cities, placing them at the core of industrial aggregation and development. As such, campuses will play a vital role in the implementation of dual-carbon strategies.
Nearly 17,000 campuses contribute to over half of China's industrial output and consume nearly 70% of the national industrial energy. Industrial campuses alone account for 31% of the country's total carbon emissions. To promote low carbon transformation, the State Council of China published the Action Plan for Carbon Dioxide Peaking Before 2030. The plan proposes the selection of 100 typical pilot cities/campuses and supporting them with policies, funds, and technologies to facilitate their carbon neutrality.
Thus it can be seen that there is a huge market space for zero-carbon smart campuses. The global investment into energy transition is predicted to reach US$131 trillion by 2050; China's investment alone will reach CNY138 trillion (nearly US$22 trillion), and over CNY1 trillion will be invested to zero-carbon smart campuses during the 14th Five-Year Plan (2021–2025).
Amid this progress, campuses are facing significant challenges. While confronted with various complex business requirements, campuses lack top-level designs, mature technology systems, and clear business models. Systematic methodologies and ecosystem-based operations are urgently needed to help campuses keep up with the pace and goals of green transformation.
The T3 development model provides a viable solution. The model envisions zero-carbon smart campuses not as a static concept but a phased and dynamic process of evolution. The first phase is smart campus (low carbon) , where distributed energy resources are adopted to promote energy saving and efficiency. The second phase is smart energy campus (near zero-carbon) , during which, campuses see the development of a zero-carbon smart energy system. The third phase — zero-carbon smart campus (net zero-carbon) — integrates multi-energy complementarity and energy efficiency along with full lifecycle carbon management, carbon energy big data, and business model optimization. This model creates a clear development path for today's campuses. Each campus can draw on the local energy resources to develop phased objectives and clear paths toward zero-carbon, energy, and digitalization transformations.
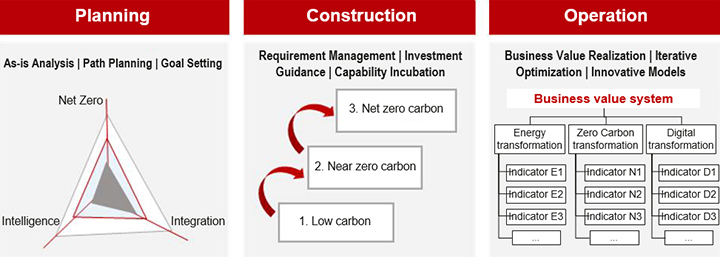
T3 Transformation: Integration of Campus Planning, Construction, and Operations
Building of zero-carbon smart campuses requires coordination among energy, zero-carbon, and digital transformations. They should follow an integrated plan in terms of planning, construction, and operation. Specifically, energy transformation should address everything from energy production and transmission to consumption, dispatch, and transaction. Zero-carbon transformation supports the entire process of management and optimization for campus carbon emissions. Finally, digital transformation facilitates clean energy transformation and efficient resource operation.
The T3 development model can help enterprises analyze their status quo, plans, and objectives. We can also manage requirements from various points of view, guide investment, and promote phased progress. At the operation stage, we can accumulate capabilities, optimize business models, and achieve iterative upgrades. T3transformation will promote the synergy and value-centered integration of energy, information, and carbon emission flows. This will in turn help realize multiple values – management being intelligent, energy being efficient and complementary, operation being decarbonized, and carbon-energy transaction being online.
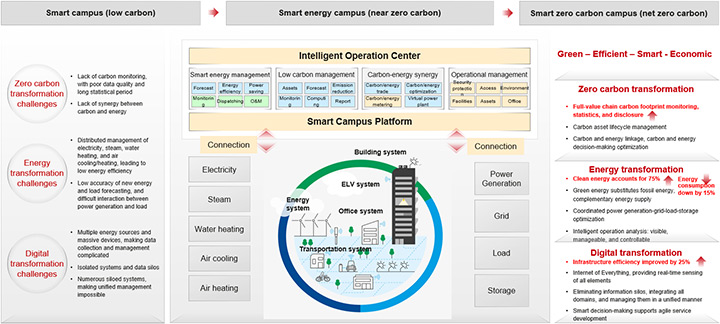
Blueprint Architecture for Zero-Carbon Smart Campuses
A zero-carbon smart campus solution should facilitate green and intelligent operations by integrating all subsystems, multiple energy resources, as well as power generation, grid, load, and storage, to save energy and improve efficiency while reducing carbon emissions of Scope 1 and Scope 2. Negative emissions technologies and carbon transactions will help reduce carbon emissions, while CCUS and carbon sink will be deployed to achieve carbon neutrality.
Digital platforms will be the foundation of such a solution. Cloud-pipe-edge-device collaboration can interconnect and complement energy and carbon management, while smart energy big data technologies will support intelligent micro-carbon management, carbon-energy synergy, and intelligent campus operations. Together, they can help build smart and agile campuses that are green and efficient, where all domains are converged.
Based on Huawei's concept of "ubiquitous connectivity + digital platform + pervasive intelligence", the T 3 development model promotes the digital transformation of campuses by developing ICT infrastructures that support cloud-edge-device collaboration. We will work with global customers and partners using unified platforms and ecosystem. Together, we can create new opportunities and values, help build a green, low-carbon, safe, and efficient modern integrated energy system, and support the achievement of the Dual Carbon goals.

Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the official policy, position, products, and technologies of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. If you need to learn more about the products and technologies of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd., please visit our product pages or contact us.