This site uses cookies. By continuing to browse the site you are agreeing to our use of cookies. Read our privacy policy>
![]()
This site uses cookies. By continuing to browse the site you are agreeing to our use of cookies. Read our privacy policy>
![]()
Enterprise products, solutions & services
Nowadays, technologies such as cloud, artificial intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), and 5G are being implemented on a larger and larger scale. Meanwhile, global branch interconnection has become a must for many multinational companies. These trends are driving demand for multi-cloud and multi-branch interconnection.
The ramping up of digital transformation as well as emergence of many external business and technical factors — such as cloud computing, network virtualization, and network-as-a-service (NaaS) — have far-reaching impacts on both the service model and network architecture of traditional enterprise WANs. Against this backdrop, traditional enterprise WANs are facing a series of new challenges:
Booming service cloudification: The vigorous development of public clouds has made more and more enterprises consider building public cloud–based IT systems for reduced construction costs and shortened construction period. For example, finance and government organizations are increasingly constructing private clouds to store and process important services. In addition, because enterprises use WANs to access software-as-a-service (SaaS) applications, such as office software and databases, they have higher demands on WAN bandwidth. Moreover, the transmission quality of enterprise WANs becomes critical to ensuring cloud application experience of enterprise customers.
Surge in applications: With the rise of cloud and digitalization, we see explosive growth in both the number and types of enterprise applications, such as voice, video, file transfer, email, and SaaS. However, these applications have varying requirements on link quality. In scenarios where traditional leased lines are deployed, enterprises cannot ensure service awareness or detect the application status. Therefore, when link congestion or quality deterioration occurs due to traffic bursts, the QoS of key services cannot be guaranteed. To address this, rapid identification of key applications and optimized user experience are required for improved office efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Fast deployment and intelligent O&M of multi-branch networks: Nowadays, digitalization and globalization result in enterprises often having a large number of widely distributed branches, which need to be connected. Additionally, due to complex and ever-changing network requirements of different branches, professional network engineers are needed to carry out onsite network provisioning, service commissioning, and fault locating. This may result in slow network deployment and high O&M costs.
In response, Huawei offers its SD-WAN Solution that prioritizes users' service application experience. With Huawei's continuous innovations, this solution is ideal for building simplified branch interconnection networks.
Huawei's SD-WAN Solution features many cutting-edge technologies, including hybrid WAN links for flexible overlay networking. It is widely acknowledged that hybrid WAN access depends on certain key network technologies, such as overlay and VPN. The overlay technology relies on IP tunnel encapsulation for transmitting traffic transparently over different WAN links. For the VPN technology, an additional VPN field is added to an IP packet for identifying different network domains. In this way, an enterprise can isolate its private network from the public network of a carrier, and even isolate different private networks. Hybrid WAN link access ensures ultra-large files can enjoy greater transmission bandwidth on Internet links. It also provides some key applications with MPLS links as dedicated channels to ensure QoS.
Huawei's SD-WAN Solution adopts application-based intelligent traffic steering to ensure application experience. The introduction of hybrid WANs allows enterprise service traffic to be transmitted over different types of WAN links, each with a different level of network quality. This means they can provide different levels of service level agreement (SLA) indicators such as packet loss, delay, and jitter. For example, the cost of MPLS links is high and the corresponding link SLA quality is guaranteed. Despite Internet links improving and there being a growing number of applications that can offer high bandwidth, Internet links often suffer from delay and packet loss and fail to guarantee SLA, making the Internet unsuitable for delay-sensitive voice and video services. By measuring the quality of different WAN links and defining the network quality requirements of corresponding applications, traffic of different applications can be transmitted over WAN links that meet SLA quality requirements. Plus, by defining traffic steering policies, the traffic of high-value applications can be preferentially transmitted over high-quality WAN links.
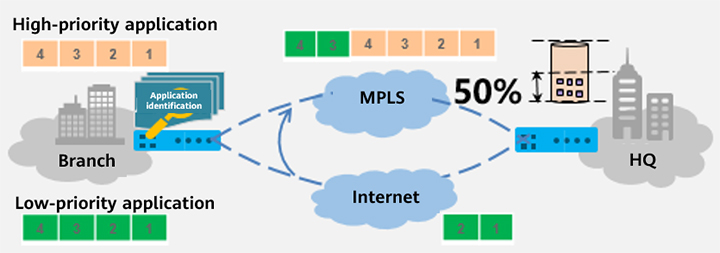
Intelligent traffic steering
Application-based traffic steering is only possible if there are WAN links that meet application SLA quality requirements. When the quality of a WAN link deteriorates significantly, for example, packet loss or long delay occurs, WAN optimization technologies need to be used to improve network fault tolerance and ensure data transmission quality. Huawei's multi-fed and selective receiving technology is a case in point. This technology increases packet redundancy by replicating one or more copies of original packets, and transmits the redundant packets over multiple paths to further enhance packet loss mitigation. After receiving the packets, the receive end sorts and deduplicates the packets, thereby achieving low-latency and high-reliability packet forwarding.
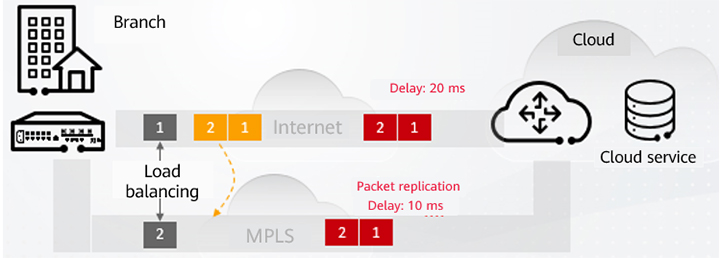
Multi-fed and selective receiving
Huawei's SD-WAN Solution uses iMaster NCE-Campus (management and control platform) to implement centralized network management and visualization for simplified O&M. The system provides the network-wide monitoring function to obtain branch link status in real time, visualizing the entire network's status. Besides this, it provides different O&M modes to give users minimal network permissions and grant access permissions by user role. In addition, this system integrates various fault diagnosis tools for application-level network quality analysis, rapidly demarcating complex network faults. All of these automated and intelligent O&M capabilities make Huawei's SD-WAN Solution ideal for improving O&M efficiency at reduced management costs.
Thanks to continuous innovations to its AR product family, Huawei provides its all-new hyper-converged gateway for small- and medium-sized enterprise branches: NetEngine AR5710. The NetEngine AR5710 supports AC power supply through a single power module and GE access. These features enable the device to be flexibly deployed in small- and medium-sized enterprise branches, slashing branch interconnection costs. This sophisticated device also supports enterprise-level security. In addition to enhanced branch security functions such as IPS, antivirus, and URL filtering, the AR5710 supports the configuration of security policy groups for more fine-grained security management and control. Moreover, with In-situ Flow Information Telemetry (IFIT)-based application-level link quality detection and interworking with Huawei iMaster NCE-CampusInsight, the AR5710 is capable of visualizing E2E application transmission quality. As a hyper-converged gateway integrating SD-WAN, routing, switching, and security, Huawei NetEngine AR5710 can further simplify branch networking, service provisioning, and O&M.

NetEngine AR5710-H8T2TS1
As one of the most popular technologies in the network field, SD-WAN is profoundly changing enterprise WAN and IT architectures. Indeed, its application has huge promise in multi-cloud and multi-branch interconnection. In order to make real progress and reap the benefits, all industry players need to work together and implement practical explorations to facilitate building simplified and high-quality multi-cloud and multi-branch interconnection branch networks through continuous innovations.
Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the official policy, position, products, and technologies of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. If you need to learn more about the products and technologies of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd., please visit our website at e.huawei.com or contact us.