Produkty, Rozwiązania i usługi dla przedsiębiorstw
Digital transformation is sweeping across all industries, and the healthcare industry is no exception. Nowadays, smart healthcare applications — including mobile ward rounds, Electronic Medical Record (EMR), mobile X-ray image reading, and smart beds — gain momentum, posing higher requirements on the quality of healthcare networks.
As such, the healthcare industry urgently needs to upgrade traditional wireless networks to the next generation. However, they are struggling to address challenges in three aspects: signal quality, terminal roaming, and Operations and Maintenance (O&M) costs.
• Poor Wi-Fi coverage and severe interference compromise user experience. Mobile ward rounds, EMR query, and image reading anytime and anywhere with handheld Personal Digital Assistants (PDAs) become the new normal. This puts a huge strain on traditional wireless networks that suffer from issues such as signal coverage holes and Wi-Fi interference.
• Packet loss leads to frequent service interruptions during terminal roaming. During the roaming of medical mobile terminals, a packet loss rate of more than 1‰ often leads to many issues, for example, as low as 1 Mbit/s bandwidth and medical software suspension.
• Siloed deployment of Wi-Fi and IoT networks leads to high costs and difficult O&M. The healthcare industry sees a growing number of IoT applications: infusion management, personnel positioning, and baby theft prevention, to name a few. In this context, independent deployment of IoT networks means more than doubled costs.
To address these challenges, the healthcare industry looks for a high-quality wireless network needed for smart healthcare. This new wireless network should stand out for the following three unique features:
• Ultimate wireless network experience: The wireless network delivers full signal coverage without blind spots, high network bandwidth, low latency, interruption-free roaming, and minimized Wi-Fi signal interference, ultimately ensuring a better user experience.
• Wi-Fi & IoT convergence: Wi-Fi and IoT networks can be converged and deployed in a unified manner to minimize network construction costs.
• Secure isolation of the internal, external, and IoT networks: The internal, external, and IoT networks are physically isolated to ensure network information security.
In keeping up with this trend, Huawei launched its next-generation Zero-Roaming Distributed Wi-Fi Solution at the Mobile World Congress (MWC) 2023. This future-proof solution helps address the challenges faced by today's healthcare industry by building high-quality smart healthcare networks with always-on services.
The zero-roaming distributed Wi-Fi architecture consists of 1 Distributed Access Point (DAP), 8 Optical Radio Units (ORUs), and 64 Antenna Units (AUs) and leverages Huawei's innovative ultra-long hybrid cables to implement deployment as far as 500 meters. This innovation enables one AP to cover as many as 64 rooms and paves the way for building a wireless network with three unique features: zero roaming, wide coverage, and tri-network isolation and converged deployment.
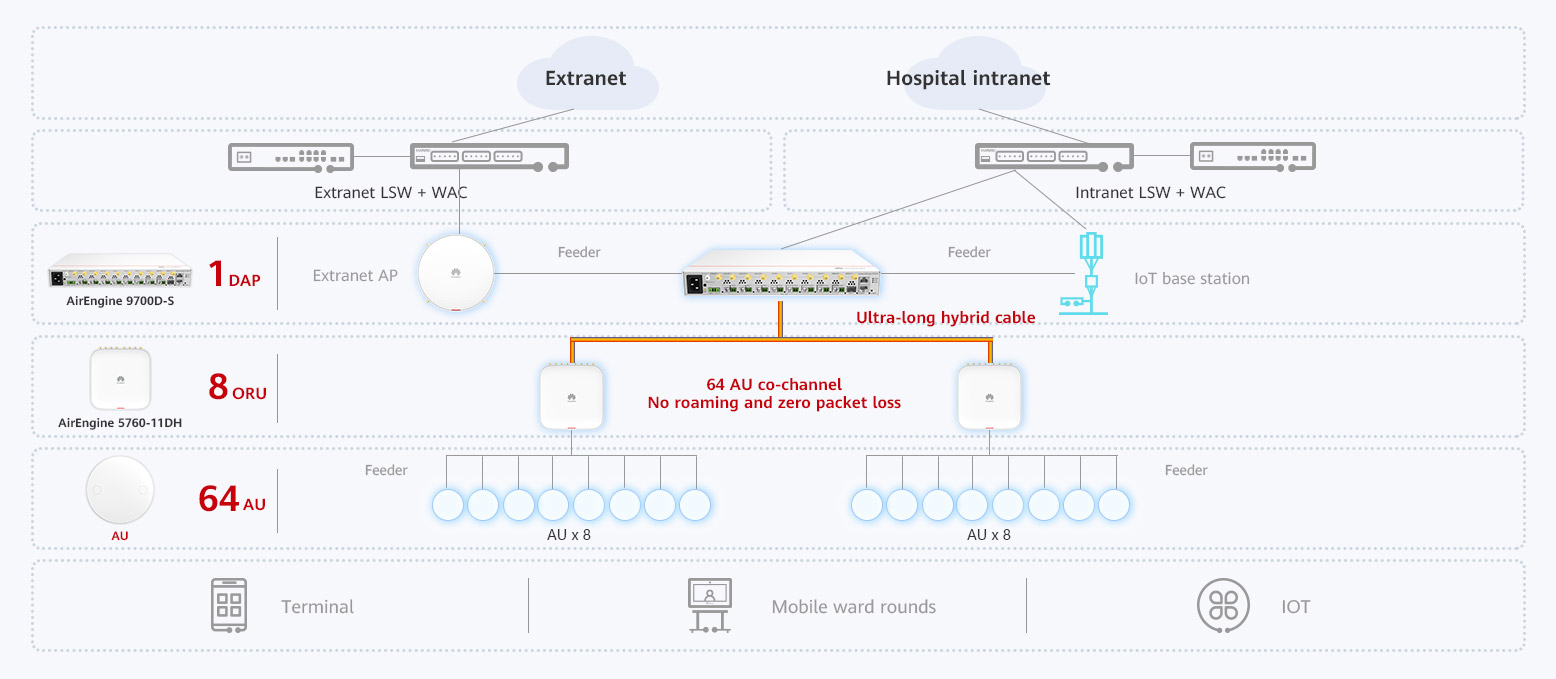
Figure 1 Zero-roaming distributed Wi-Fi architecture
Zero roaming: One DAP can connect to eight ORUs at most. Then, each ORU can connect to a maximum of eight AUs through super-flexible feeders. This means the entire system supports up to 64 AUs. That's why one single AP can cover 64 hospital wards. Furthermore, all the 64 AUs work on the same channel, enabling zero roaming, zero packet loss, and always-on services for moving terminals within the coverage of this AP.

Figure 2 Adjacent Wi-Fi devices working on different channels in traditional solutions

Figure 3 Adjacent AUs working on the same channel in the zero-roaming distributed Wi-Fi solution
Wide coverage: The DAP uses innovative ultra-long hybrid cables to provide on-demand Wi-Fi coverage across building floors at a maximum distance of 500 meters. In particular, one single DAP supports a maximum of eight ORUs, enabling one such AP to cover an entire building floor.
Tri-network isolation and converged deployment: IoT base stations and external network APs feed signals into the DAP, which then transmits the signals to ORUs through hybrid cables. In this way, the internal, external, and IoT networks are converged into one network but are physically isolated. This, in turn, reduces network construction costs by 60% without compromising network security or reliability.
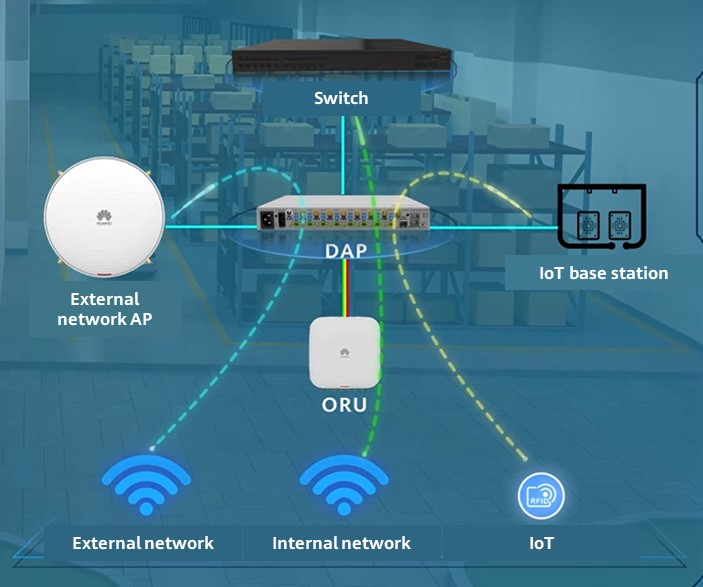
Figure 4 Implementation of zero-roaming distributed Wi-Fi
With these traits, Huawei's Zero-Roaming Distributed Wi-Fi Solution is a great fit for the healthcare industry to keep up with trends and meet ever-changing service needs. With this solution, the healthcare industry is well poised to build a next-generation Wi-Fi network with stand-out features such as zero roaming, wide coverage, and tri-network isolation and converged deployment. The resulting benefits include over 50% higher medical care efficiency, smooth medical services anytime and anywhere, and more.
Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the official policy, position, products, and technologies of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. If you need to learn more about the products and technologies of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd., please visit our website at e.huawei.com or contact us.