This site uses cookies. By continuing to browse the site you are agreeing to our use of cookies. Read our privacy policy>
![]()
This site uses cookies. By continuing to browse the site you are agreeing to our use of cookies. Read our privacy policy>
![]()
Enterprise products, solutions & services
At HUAWEI CONNECT 2022 in Dubai, Huawei and IEEE-UAE Section jointly released the L3.5 Data Center Autonomous Driving Network White Paper, which provides deep insight into the architecture, key capabilities, and typical application scenarios of L3.5 autonomous driving networks (ADNs) in data center scenarios, as well as deployment practices for key sectors such as finance, public service, and manufacturing.
According to the white paper, some enterprises have multiple data centers that use different architectures and are on multiple heterogeneous clouds, and multi-cloud and multi-vendor network products and solutions vary greatly:
• Distinct network models, command lines, and interfaces are used.
• The network management system of a vendor can manage only the vendor's own products. This leads to siloed management within enterprise data centers.
• Changes often involve networks built with devices of multiple vendors and configurations are performed on a per-vendor basis. In addition, vendors' automation capabilities vary, leading to a heavy manual workload.
For enterprises DCNs to truly move towards highly autonomous networks, these challenges must first be solved.
L3 implements conditional autonomy within a single network. A major milestone on the way to evolving from L3 to L4 is L3+, also called L3.5, where L3 is implemented across multi-cloud, multi-data center, and multi-vendor networks.
Network as a service (NaaS) capabilities are used for interconnection with enterprise IT management systems for flexible orchestration and invocation to integrate with enterprises' IT processes. This helps achieve service intent-driven data center network-wide conditional autonomy.
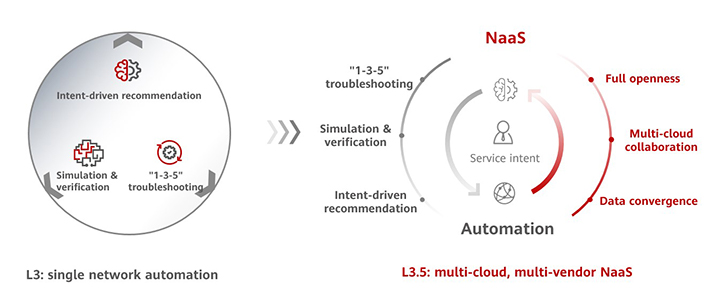
Leveraging iMaster NCE — an ADN management and control platform — Huawei's L3.5 Data Center Autonomous Driving Network Solution addresses the preceding challenges with the following key features:
• Low-code workflow orchestration: The runbook intent orchestration platform provides more than 100 generic NE models for flexible orchestration through simple drag-and-drop operations. Service workflows can be flexibly defined based on service requirements and published as APIs to quickly interconnect and integrate networks with service systems. By consolidating service-oriented network capabilities, the intent orchestration platform reduces the number of work orders by 90% and design workload by 70%, slashing the service rollout period from months to minutes.
• Open programmability platform: In the southbound direction, the Agile Open Container (AOC) — Huawei's open programmability platform — dynamically loads third-party drivers as plug-ins to implement open interconnection with multi-vendor devices.
• Unified data modeling: Unified data modeling is implemented for heterogeneous and multi-vendor networks, extending unified management and automation from a single network to public clouds, private clouds, and on-premises clouds. This helps provision cross-cloud networks in seconds, achieve network-wide visualization and simulation, and ensure error-free configuration changes.
• Unified O&M of applications and networks: Powered by Telemetry technology, iMaster NCE collects more than 100 types of data in real time. It uses data virtualization technologies to correlate data from the service perspective and establish a unified data service catalog. Plus, iMaster NCE combines entries in data catalogs and orchestrates them into service scenario-specific data on demand. This allows users to centrally invoke data without having to be aware of the underlying data model.
There is still a long way to go before true ADN is achieved. To help reach this goal, in addition to working on standards and technologies, all stakeholders need to continuously deepen the ADN evaluation system to drive network upgrades towards automation and intelligence and evolve across generations.
In recent years, Huawei has remained committed to researching and making breakthroughs in key ADN technologies and exploring typical scenarios, and has achieved remarkable results. Huawei is open to partnering with industry players to build consensus, apply innovative approaches, and move forward together to promote the large-scale application of network AI technologies and advance DCNs into the ADN era featuring agile business, ultimate experience, and efficient O&M.
Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the official policy, position, products, and technologies of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. If you need to learn more about the products and technologies of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd., please visit our website at e.huawei.com or contact us.