Intelligent WAN Solution Passes the EANTC Test
In January 2020, the European Advanced Networking Test Center (EANTC) conducted a three-week independent test on Huawei's intelligent WAN solution for the all-service intelligence era, covering. The test cases are designed from the aspects of super capacity, intelligent experience, and autonomous driving. Using Huawei NetEngine 8000 X/M series routers and iMaster Network Cloud Engine (NCE), the test was successfully carried out, which impressed EANTC test experts. The following figure shows the network topology.
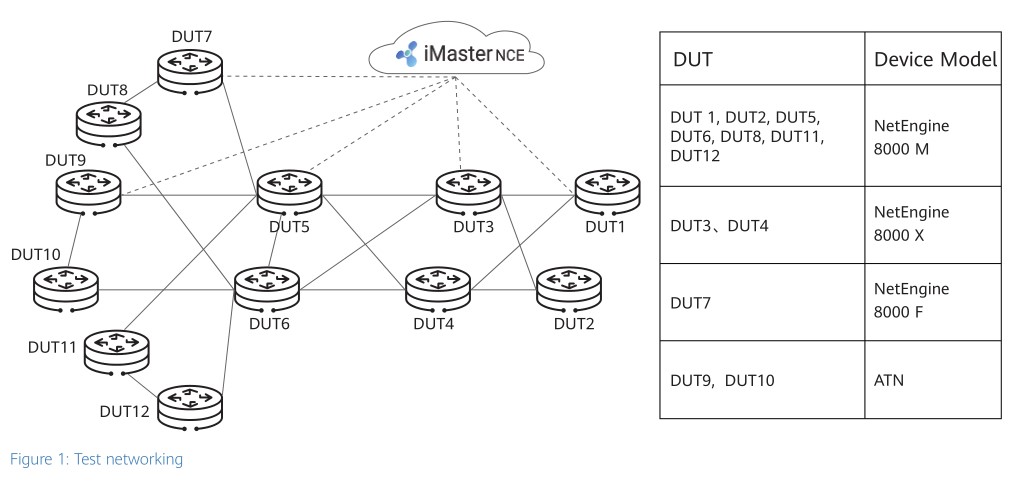
Huawei's NetEngine 8000 series products support full-series access-side interfaces, such as PCM, E1, SDH, GE, and 10GE, as well as network-side 100GE and 400GE interfaces, meeting the requirements of extensive interfaces and high bandwidth for enterprise services and allowing on-demand access for production and office services. iMaster NCE manages network slices through the entire lifecycle, featuring flexible bandwidth adjustment and hard isolation of slice resources to ensure the bandwidth of critical services.
E2E 400GE ensures optimal cost per bit. According to a report published by LightCounting, the demand for 100GE interfaces will continue to increase over the next two years, and the demand for 400GE interfaces will increase rapidly. The test conducted by EANTC focuses on the line-rate forwarding capabilities of 400GE and 100GE interfaces. It uses a tester leveraging the RFC 2544 test suite to simulate data traffic. Both the device and tester are directly connected to each interface in order to test the forwarding capabilities and power consumption of 400GE and 100GE interfaces. The test results show that Huawei NetEngine 8000 X8 4T board supports line-rate forwarding and it consumes only 0.28 W/G of power, 30 percent lower than the industry average.
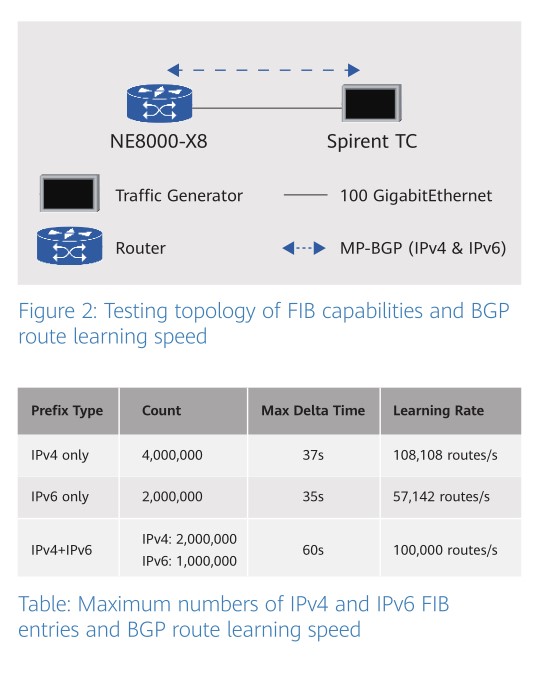
A WAN is connected to a large number of external and internal enterprise networks and therefore has high requirements for FIB capacity. This test verifies the maximum FIB capabilities of the NetEngine 8000 X series, which is connected to Spirent TC. The test result shows that the maximum number of IPv4 entries is 4M, the maximum number of IPv6 entries is 2M, and the learning speed is 10k per second, outperforming the industry average.
Network slicing allows flexible bandwidth adjustment, and hard resource isolation guarantees bandwidth. On a traditional network, all services share bandwidth resources and preempt each other. As a result, the bandwidth for key services can’t be guaranteed. The hard resource isolation solution can ensure the development of 5G vertical industries and enable numerous industry networks over one physical network. In the EANTC multi-vendor interoperability test held in 2019, some basic tests were performed on the hard slicing technology. However, the automated full lifecycle slice management has always been a major concern. The test conducted in 2020 verifies the slice management capability of iMaster NCE. The test results show that Huawei iMaster NCE implements GUI-based full lifecycle slice management, including creating, modifying, and deleting slices. In the test, iMaster NCE was used to create two hard slices: one to carry URLLC services, and the other to carry eMBB services. A tester was then used to simulate a large amount of burst traffic in order to exceed the allocated bandwidth on one slice. This resulted in many of packets being lost on this slice, but the service traffic on the other slice remained normal without experiencing any congestion or packet loss. Subsequently, a new slice was created on and then deleted from iMaster NCE. This operation didn’t affect normal service flows on the two original slices.
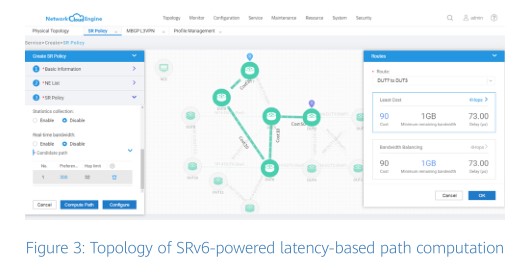
In the all-service intelligence era, office and production services are carried on one network, but different industries and applications have different latency requirements. For example, smart grid requires a transmission latency of less than 15 ms. Because the traditional networks use the best-effort forwarding mode, the forwarding path can’t be controlled and the end-to-end latency can’t be ensured. This means traditional networks can’t meet application requirements in the industry. The EANTC test is designed to verify whether Huawei's intelligent WAN solution addresses this problem. In this test, SRv6 is used to implement intelligent traffic steering and latency commitment. Different latencies are set for different links to check whether the forwarding path on an End-to-End (E2E) network meets the latency requirements. The test results show that Huawei routers and iMaster NCE use SRv6 Policy to implement path selection through latency-based path computation. This meets the requirements of latency SLA, as well as other SLAs such as link costs, bandwidth, and specific paths. iMaster NCE can also automatically adjust and optimize services in real time to ensure SLAs if the packet status changes, for example, a link is interrupted. No packets are lost during service adjustment and optimization.
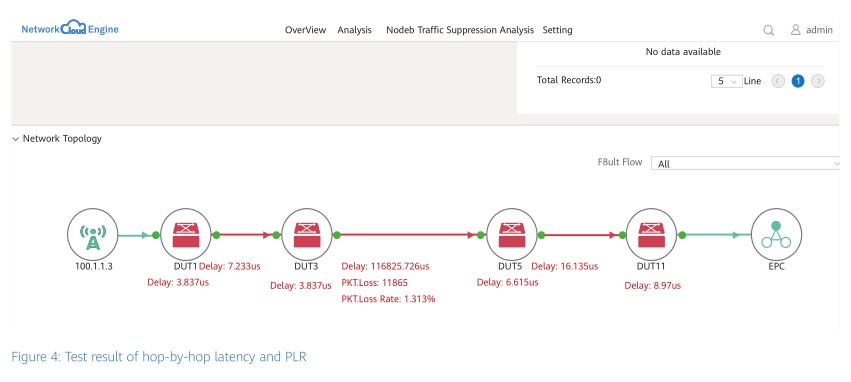
Traditional network O&M lacks refined data collection technologies and therefore service quality cannot be accurately learned and faults cannot be quickly located. This test verifies the industry's first In-situ Flow Information Telemetry (iFIT) solution by simulating packet loss caused by link congestion on forwarding paths. The test results show that Huawei routers can report real service data to iMaster NCE through iFIT in an E2E manner, and iMaster NCE displays information about service quality (such as latency and packet loss rate) in real time. The results also show that it takes no more than one minute for iMaster NCE to detect that the number of lost packets exceeds the preset threshold. iMaster NCE immediately triggers iFIT hop-by-hop detection after detecting the threshold-crossing occurrence. The forwarding path and SLA change information of the service flow are displayed on the GUI of iMaster NCE in real time, and faulty nodes are clearly displayed. In addition, Topology-Independent Loop-Free Alternate (TI-LFA) is used to achieve protection switching of faulty nodes within 50 ms.
This test verifies that Huawei's intelligent WAN solution features super capacity, intelligent experience, and autonomous driving. E2E 400G is used to guarantee the optimal cost per bit. Network slicing is used to flexiblely adjust bandwidth for 100 percent bandwidth guarantee. In addition, key technologies, such as constraint-based SRv6 Policy path computation and dynamic optimization and iFIT, the next-generation OAM technology for real-time monitoring and fast fault demarcation and locating, lead WAN into the all-service intelligence era.
"In the EANTC test, we simulated the real network evolution requirements of service providers and tested the issues that concern carriers during the construction of 5G converged transport networks. We evaluated a wide range of functional aspects of Huawei's SRv6 implementation across the NetEngine 8000 and ATN family and NCE — with impressive results. Huawei has demonstrated its industry-leading capabilities, providing more intelligent IP network experience and simplifying network operations and maintenance through NCE," said Carsten Rossenhoevel, Managing Director of EANTC.
EANTC (European Advanced Networking Test Center) is internationally recognized as one of the world’s leading independent test centers for telecommunication technologies. Based in Berlin, Germany, the company offers vendor-neutral consultancy and realistic, reproducible high-quality testing services since 1991. Customers include leading network equipment manufacturers, tier-1 service providers, large enterprises and governments worldwide.
Testimony from EANTC:
In the EANTC test, we simulated the real network evolution requirements of service providers and tested the issues that concern carriers during the construction of 5G converged transport networks. We evaluated a wide range of functional aspects of Huawei's SRv6 implementation across the NetEngine 8000 and ATN family and NCE — with impressive results. Huawei has demonstrated its industryleading capabilities, providing more intelligent IP network experience and simplifying network operations and maintenance through NCE.
— Carsten Rossenhoevel, Managing Director of EANTC
