AIFW: Empowering Border Defense
As digital transformation is sweeping across the globe, the accompanying unprecedented connections, explosive data, and mushrooming intelligent applications are redefining the way we live and work. Amid this trend, interactions between individuals, between individuals and enterprises, and between enterprises are flourishing more than ever. This, in turn, boosts economic and social development.
Extensive applications of cloud computing and big data analytics are accelerating digital transformation of enterprises, and intelligent service upgrades are driving the revolutionization of enterprise networks. All these trends have created unparalleled challenges for network security. Moreover, cyber criminals won’t stop in their attempts to gain access to personal privacy, enterprise confidentiality, and computing resources. Everything has its advantages and disadvantages, and digitalization is no exception. While it adds convenience to our lives, it also leads to many security risk.
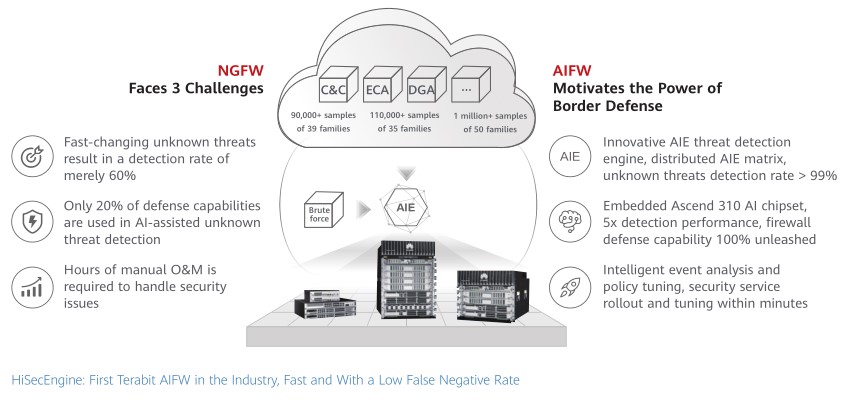
Gartner defined Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFWs) in 2009, and since then, these security devices have become increasingly important and used to meet numerous challenges. The first challenge is coping with the ever-increasing unknown threats. Even known threats evolve into a wide range of unknown threat variants to bypass security. Such variants are difficult for NGFWs to detect based on signatures. The second challenge is defending against multi-faceted threats. The rapid development of 5G and IoT allows for an increasing number of devices to connect to the Internet. However, these devices can be vulnerable to hackers to initiate multi-faceted attacks. According to a survey conducted by Forrester, 49 percent of enterprises are undergoing many more intranet threats than ever before. This indicates that the scope prone to attacks is widening, namely, attacks may come from both external and internal networks. By exploiting these vulnerabilities, attackers can initiate sophisticated attacks that form a comprehensive attack chain, from initial compromise, remote control, and lateral movement, to theft and damage.
Traditional NGFWs, however, cannot cope with these issues and are calling for a revolutionary upgrade.
Recently, AI technologies keep on developing iteratively. In addition, new technologies such as Deep Leaning (DL) can make optimal use of big data accumulated in this mobile Internet era to make breakthroughs in learning accuracy. Applying AI technologies into all sectors can significantly improve the production and life efficiency. The network security domain also witnesses wider applications of AI technologies, most of which are built on big data-powered security threat analysis that is typified by high investments, discouraging most customers from deploying it.
However, in addition to these domains, AI technologies can also be applied to firewalls to increase network security. These AI technologies are highly effective at mapping mass information to high-dimensional space through their superb information abstraction capabilities. The generalization and reasoning capabilities developed in this process open up new opportunities for security protection. Moreover, AI technologies can perform operations at a higher efficiency than manned operations and sophisticatedly interpret the patterns of threats and attacks. For example, supervised and unsupervised learning can detect ever-evolving malicious files at a higher efficiency, detect compromised hosts and devices as well as encrypted malicious traffic, and identify malicious behaviors such as low-frequency or distributed brute force cracking. In addition, the AI learning model can make full use of mass data, generate defense models based on scenario data analysis and training, and continuously upgrade and evolve the models in line with real-time data on the live network. Therefore, AI technologies are the optimal choice to eliminate the shortcomings of traditional NGFWs, enhance threat detection capabilities, and automate threat handling.
Fully unleashing AI technologies in the network security domain requires substantial computing power. Relying only on the service processing CPU of firewalls, the traffic forwarding capability of firewalls will drastically decrease once AI is enabled. Therefore, the AI chip needs to be embedded into firewalls to meet the high requirements for computing power.
After in-depth research and stringent verification, Huawei has successfully launched brand-new lineups of HiSecEngine USG6000E and USG12000 AIFWs. These two AIFWs series are equipped with Huawei’s exclusive AI-powered threat detection engine — AIE — to handle threats in real time at the network edge and accurately detect more than 99 percent of unknown threats. Furthermore, Huawei HiSecEngine AIFWs have built-in AI chips to deliver up to 8T FLOPS of computing power, achieving a fivefold performance increase in unknown threat detection without deteriorating their traffic forwarding capability. As such, attack defense capabilities of AIFWs are fully unleashed.
Huawei HiSecEngine USG6000E series AIFWs were officially launched in January 2019. As verified by authoritative organizations in China, they can detect threats that cannot be detected by traditional NGFWs as well as external connections created by infected hosts through the Domain Generation Algorithm (DGA). As verified, the USG6000E can detect 99,715 out of 100,000 malicious domain names in the 41 DGA families, achieving a detection accuracy of 99.7%. In addition, the future-proof AIFWs can accurately detect 100 percent of 38 types of Remote Access Trojan (RAT) families and 34 types of malicious behavior families in encrypted communications.
Since their debut, more than 50,000 HiSecEngine USG6000E series AIFWs have been delivered and have helped users in all sectors detect and eliminate various new threats, receiving high recognition in the market.
“The industry’s pioneering AIFWs launched by Huawei successfully overcome the limitations of static rule engines on traditional NGFWs, enhance threat detection capabilities, and address challenges facing security O&M through enabling automation,” said Denzel Song, President of Huawei Security Domain. “The AIFWs also leverage AI chips to deliver significantly stronger intelligent detection capabilities, laying a solid foundation for in-depth implementation of AI technologies into security gateways. With AI, network devices and the cloud can collaborate with each other, boosting the development of a security interaction ecosystem; a much more solid security platform can be built through multi-party collaboration, safeguarding enterprise networks.”