5G AR Routers: Building Ultra-Broadband and High-Quality Enterprise WANs
Wide Area Networks (WANs) are crucial for cloud-based enterprise service deployment, cross-regional interconnection, and network interaction with the outside world. With the advent of 5G, enterprises are undergoing comprehensive intelligent service upgrades and accelerated digital transformation. This means that the data volume on enterprise WANs will increase dramatically. As such, enterprise WANs face unprecedented challenges in adapting to network service requirements in the 5G era and translating 5G features into network resource dividends.
In response to such immense challenges, Huawei has launched NetEngine AR series routers — next-generation SD-WAN-capable 5G enterprise routers. With a wide range of features, these routers provide powerful 5G uplink capabilities, deliver three times the industry average forwarding performance, and integrate innovative Adaptive Forward Error Correction (A-FEC) for video optimization. NetEngine AR series will be able to deliver the optimal service experience and transmit ever-increasing amounts of WAN data, as requirements continue to increase over the next three to five years.

The 4G era is typified by to-consumer (2C) applications, so most data transmitted over the network is downlink traffic. In the 5G era, where all things are connected, massive amounts of to-business (2B) industry application data will be generated, creating new demands for higher uplink bandwidth and lower latency.
For example, with 5G, banks can deploy interactive robots, smart teller machines, Financial Capsules, and Artificial Intelligence (AI) in customer service, enabling traditional branches to transform into smart marketing- and service-oriented branches. To achieve these innovative services, WANs with higher bandwidth and lower latency are required. However, traditional private lines provide only 2 Mbps to 4 Mbps bandwidth, while 4G links are used only as backup links due to insufficient bandwidth and poor stability.
Huawei’s 5G AR routers provide a viable solution to make a difference. They use a first-of-its-kind commercial 5G dual-mode chip — Balong 5000 — which incorporates Huawei’s futuristic 5G Super Uplink technology. This greatly improves 5G transmission rates and reduces air interface latency.
The routers also use 5G New Radio (NR) to support two duplex modes — Frequency Division Duplex (FDD) and Time Division Duplex (TDD):
FDD: Data is transmitted on two independent and symmetric frequency channels in upstream and downstream directions. Like a two-way road, traffic in both directions doesn’t interfere with each other.
TDD: The uplink and downlink data is transmitted on the same frequency channel by assigning transmitted and received signals in separate timeslots. This is like a reversible lane, in which traffic direction is reversed by time segment.
By combining TDD and FDD, Huawei’s 5G Super Uplink technology eliminates the need to transmit uplink data according to timeslots. When uplink data is transmitted in the 3.5 GHz TDD frequency band, no data goes over the FDD uplink frequency band. This makes full use of the 100 MHz bandwidth provided by the 3.5 GHz band. Meanwhile, when downlink data is transmitted in the 3.5 GHz band, the FDD frequency band is used to transmit uplink data. This implements timeslot-based traffic diversion between FDD and TDD and ensures that uplink data is transmitted in all timeslots.
5G Super Uplink technology innovatively combines TDD and FDD and increases the 5G uplink rate by 20 percent to 50 percent. This makes it ideal for sectors requiring a high uplink bandwidth, such as smart banking, telemedicine, and smart manufacturing. Huawei’s 5G AR routers are also backward compatible with 3G and 4G, and support both non-standalone (NSA) and standalone (SA) networking.

The number of network terminals connected to enterprise networks sees a ten-fold increase each year. Today, 85 percent of enterprise services can already be deployed on the cloud, while enterprises are evolving toward full cloudification. With the advent of 5G, enterprises may launch new intelligent services or even develop brand-new service systems at any time. The resultant rapid growth in WAN traffic makes WAN links more prone to congestion, failing to guarantee user experience of key applications. With Software-Defined Networking (SDN), SD-WAN uses technologies such as application identification, intelligent dynamic traffic steering, Quality of Service (QoS), and WAN optimization to optimize and ensure the service-layer application experience.
The full-series SD-WAN-capable 5G AR routers monitor network quality in real time. They dynamically and automatically select the optimal WAN link that meets the Service Level Agreement (SLA) requirements of applications, while maximizing the overall usage of WAN links. With SD-WAN, 5G AR routers enable multiple traffic steering methods, including link quality-, load balancing-, and application priority-based traffic steering. This ensures that traffic of key applications is always transmitted on the optimal link, and enterprise customers have a high quality application experience.
Since the COVID-19 outbreak, the enterprise business model changed substantially. Contactless businesses and services, such as online education, remote office, and telemedicine, have quickly gained in popularity. At Huawei, for example, the number of remote office employees has increased exponentially, and the number of WeLink video conferences doubled daily at the beginning of the outbreak. Meanwhile, 270 million students staying at home in China have been taking over 24,000 different e-courses through 22 online education platforms. As a result, video services have gained importance in a variety of sectors. However, video is a packet loss-sensitive service, with high requirements on WAN links that are prone to packet loss due to traffic bursts and congestion. To address the problems, 5G AR routers innovatively apply WAN optimization to ensure the SD-WAN application experience.
The industry typically uses Forward Error Correction (FEC) to ensure video streaming quality. It transmits redundant frames at the transmit end and attempts to use these to recover the lost data packets at the receive end. Huawei dove deep into application optimization algorithms and developed an innovative A-FEC algorithm. A-FEC calculates and dynamically changes the required proportion of redundant frames based on the packet loss rate and the number of consecutive lost packets. This alleviates or even eliminates the impact of packet loss on transmission. The A-FEC algorithm removes freeze frame and artifact for video applications even at a 20% packet loss. It also improves link usage.
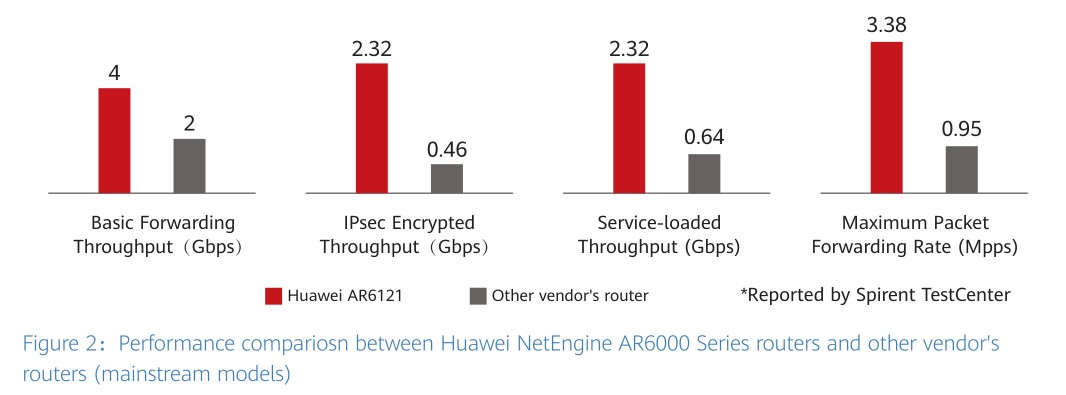
5G services require 100 times more bandwidth, and the introduction of SD-WAN further complicates service processing. When SD-WAN is enabled on a traditional router, this results in an 80 percent performance reduction. To deploy SD-WAN, enterprises require high-performance routers for a WAN upgrade. That’s where Huawei’s 5G AR routers come in. They use an innovative “multi-core CPU + Network Processor (NP)” heterogeneous forwarding architecture, marking a groundbreaking forwarding technology for enterprise branch routers. Huawei’s 5G AR routers stand out with many hardware and software innovations. In terms of hardware, Huawei’s 5G AR routers use the NP to quickly offload Layer 2 to Layer 4 traffic, efficiently forwarding basic services. The routers also integrate five hardware acceleration engines: Internet Protocol Security (IPsec), hierarchical Quality of Service (HQoS), security, Service Awareness (SA), and application optimization, further improving the forwarding performance. In terms of software, Huawei’s 5G AR routers incorporate in-house ultra-fast algorithms, maximizing the multi-core forwarding performance.
By combining these hardware and software innovations, Huawei’s 5G AR routers offer triple the forwarding performance of comparable products from competitors, as certified by Tolly. For more information, see Tolly’s test report on Huawei’s next-generation NetEngine AR enterprise routers.
The rise of 5G and SD-WAN is accelerating the pace of intelligence and cloud transformations of enterprise services on enterprise WANs. According to the China Construction Bank (CCB), their smart banks powered by 5G and SD-WAN will soon replace traditional over-the-counter banks to expand the scope of self-services and offer 327 basic financial services, greatly improving the efficiency of financial services. Behind this is the upgrade of their enterprise WANs. By using Huawei’s 5G AR routers, CCB is transforming into 5G+ smart banking, which will provide innovative services such as interactive robots, smart teller machines, Financial Capsules, and AI customer service.
When deployed at the egress of enterprise WANs, Huawei’s 5G AR routers provide ultra-broadband 5G channels and ultra-high service processing capabilities for enterprises. SD-WAN also provides an oustanding application experience and builds high-speed and super-quality WANs, facilitating the digital transformation of enterprises.