This site uses cookies. By continuing to browse the site you are agreeing to our use of cookies. Read our privacy policy>
![]()
This site uses cookies. By continuing to browse the site you are agreeing to our use of cookies. Read our privacy policy>
![]()
Продукты, решения и услуги для предприятий
Смартфоны, ПК и планшеты, носимые устройства и многое другое

AI technologies are developing rapidly. In good hands, AI could be a great productivity tool. However, in the wrong hands, AI could be exploited by hackers to launch network attacks. According to statistics of AV-TEST, the number of new malware programs observed is more than 100 million per year, which means that about 4 new malware programs are discovered per second. In the AI era, attacks are highly automated and covert. It is an urgent need to quickly and accurately identify unknown threats. To address these challenges, Huawei's Xinghe Intelligent Unified SASE Solution integrates the emulator microkernel unpacking engine and AI detection algorithms into the firewall, breaking the bottleneck of traditional signature-based detection and improving the detection rate of unknown threats to 95%.
First, we need to understand the packing technology. Packed malware is malicious code that uses compression or encryption to hide its malicious features, making it difficult to parse the malware in the static analysis phase. Once malware is packed, it is impossible to extract meaningful signatures, rendering traditional signature-based detection mechanisms ineffective.
Detecting unknown threats is difficult due to the following reasons:
• AI-driven malware variants grow explosively, with more than 330,000 new variants per day, outpacing traditional detection methods.
• More than 95% of web traffic flow over HTTPS and 86% of the advanced threats are delivered over encrypted channels, making traditional signature-based detection mechanisms ineffective.
• Advanced bypass technologies are widely used, and more than 30% of attacks bypass security inspection through obfuscation. Traditional solutions require tens of thousands of rules to defend against a single attack, increasing defense costs.
To cope with unknown threats, Huawei firewalls use AI to improve unknown threat detection capabilities. Two key technologies are used: Emulator microkernel unpacking engine and AI security detection algorithms.
The Emulator microkernel unpacking engine can accurately identify the real semantics of malware in milliseconds.
Most malware uses packing technology to avoid detection. Most of vendors use off-line third-party tools to unpack malware. This method is time-consuming and post-postmortem. When malware is detected, the damage is done.
To facilitate understanding, we compare the generation and detection processes of AI-driven variants to the security check process of dangerous prohibited items.
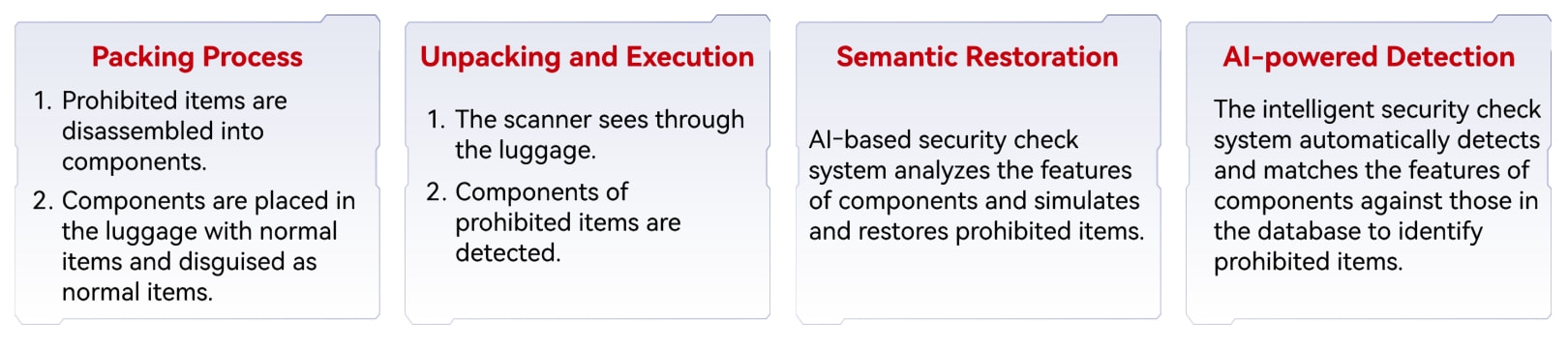
Figure 1: Analogy of AI-based unknown threat detection to security check of dangerous prohibited items
1.Malware Unpacking in Milliseconds — Seeing Through Luggage
Huawei integrates its proprietary lightweight emulator microkernel unpacking engine into the firewalls to unpack variant files in milliseconds. The engine emulates the CPU, memory, and operating system (OS) at a high speed using software to dynamically simulate the execution of malicious program code instructions. This is equivalent to conversion of ciphertext to plaintext. This process is fast to quickly complete the in-depth analysis of the OS, memory management, instruction simulation, and malware with minimum resource usage. This is the unpacking process, which is similar to the process of detecting prohibited items hidden in normal luggage through in-depth scanning during security check.
2.Semantic Restoration — Revealing the Full Picture of Prohibited Items
At this point of time, we still have no meaningful binary bytes. Semantic restoration is required. To do so, the engine uses high-performance instruction compilation and CPU cache implemented through software to accelerate the simulation process. In this way, we can securely and dynamically analyze suspicious malicious code and memory fragments in a virtually isolated microkernel in real time to identify hidden malicious behavior and accurately restore the real semantics of malware. Now we have completed the semantic restoration process. It is similar to the X-ray scanner analyzing the features of the luggage content to reveal prohibited items.
Detecting Up to 95% of Unknown Threats Using AI
After malware unpacking and semantic restoration, another key technique is required: AI security inspection algorithm.
Huawei's Intelligent Security Center on the cloud provides continuous and powerful security capabilities for AI security inspection on firewalls. It analyzes hundreds of millions of viruses and builds a dedicated AI algorithm to detect known and unknown viruses with high performance and accuracy. Firewalls can connect to the Intelligent Security Center on the cloud to update the local AI security inspection algorithm in real time to keep the defense system up to date. The built-in algorithm of firewalls can accurately identify and block unknown threats in real time. The following uses malicious file detection as an example to describe how the built-in algorithm of firewalls extracts behavior and unpacking signatures of malicious files to complete local AI detection and inference, achieving fast and accurate malware detection.
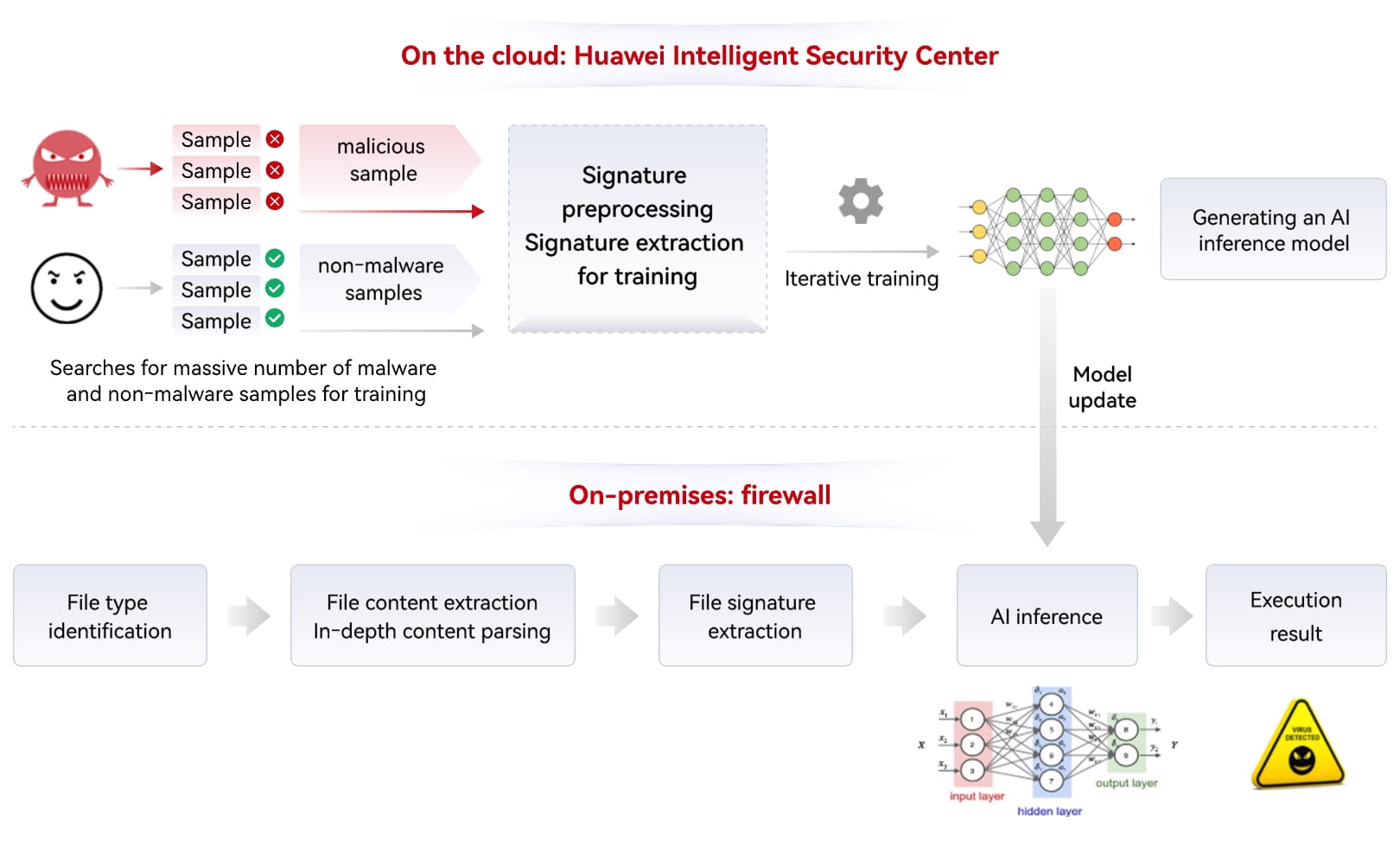
Figure 2: Endpoint-cloud collaboration for AI-based malicious file detection
In addition, the firewalls use multiple AI detection technologies at different stages to provide multi-layer protection against unknown threats.
(1) In the scanning and reconnaissance phase, the AI-based brute force cracking detection model is used to effectively defend against distributed brute force cracking attacks and protect service systems from unauthorized access.
(2) In the penetration and privilege escalation phase, the AI-based antivirus detection model is used to quickly detect a large number of malware variants.
(3) In the connection establishment and control phase, the AI-based algorithm is used to detect malicious domain names randomly generated by a Domain Generation Algorithm (DGA), which cannot be detected using the traditional domain name database. In this way, the communications between compromised and hackers are cut off to prevent sensitive data leakage. The AI-based encrypted traffic inspection model is used to identify threats in encrypted traffic without decryption. The AI-based C&C communication detection model is used to accurately identify C&C and covert channels, block hacker remote control communications, and prevent sensitive data leakage.
Huawei firewalls seamlessly integrate the Emulator microkernel unpacking engine with the AI detection algorithms to unpack malware files in milliseconds, block threats in real time, and detect up to 95% of unknown threats. In the AI era, new attacks are emerging one after another. AI defense is required to prevent AI attacks. A more efficient and intelligent cloud-edge integrated defense system is needed.
If you are worrying about unknown network threats, you might want to learn more about Huawei Xinghe Intelligent Unified SASE Solution. For more information, visit Huawei official website.
Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the official policy, position, products, and technologies of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. If you need to learn more about the products and technologies of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd., please visit our product pages or contact us.