CMB: Promoting Network Transformation, Creating the Future of Financial AI
Produits, solutions et services pour les entreprises
Akıllı Telefonlar, Bilgisayar&Tabletler, Giyilebilirler ve Daha Fazlası
Huawei’s CloudFabric data center network provides powerful support for CMB in digital transformation and digital operation reconstruction. Huawei will continue to partner with CMB to promote Retail Finance 3.0 and shape the future of financial AI.

China Merchants Bank (CMB) was founded in 1987 in Shenzhen, the city at the forefront of the reform and opening-up of China. It is the first share-holding commercial bank to be wholly owned by corporate legal entities in China. CMB is innovative in providing thoughtful services to customers. For example, CMB was the first Chinese bank to hold umbrellas for customers coming in and out of the bank on rainy days, introduce queue management systems, and offer milk to customers. Over the past 30 years, CMB has developed rapidly and was ranked No. 188 in the Fortune Global 500 list in 2019. Among the Top 1000 World Banks list in 2018 released by The Banker, an authoritative financial magazine in the UK, it was ranked No. 20 by capital, No. 12 by profit, No. 7 by Return On Equity (ROE), and No. 3 by revenue. CMB was ranked No. 1 by business performance indicators among all banks in China.
The above achievements are due to CMB’s continuous strategic transformation over the years. In terms of digital transformation, CMB specified its strategic direction and positioning of “Light Bank” and “One Body with Two Wings,” with retail finance as the main body and corporate finance and interbank finance as two wings, in 2014. In 2015, CMB outlined its mobile-first strategy and developed two apps, Mobile Banking and Handheld Life, taking CMB into the app era. In 2017, CMB proposed to use financial technology as the driving force for future transformation. This allowed CMB to change from a “customer thinking” to “user thinking” strategy. It also enabled the company to change from a “card business” to “app operation” direction, and from a “transaction thinking” to a “user journey thinking” approach. The company has been dedicated to promoting Retail Finance 3.0 and transforming from operating static transaction products to building a dynamic service ecosystem.
The main operation field of CMB has changed from branches to apps. The two apps, Mobile Banking and Handheld Life, have become the most important carriers for connecting customers to CMB and the most important platform for CMB to provide retail services. By the end of 2019, the number of Monthly Active Users (MAU) of the two apps reached 102 million. In 2018, CMB proposed to use the MAU as the “North Star Metric” to guide retail financial transformation. In the Retail Finance 3.0 era, CMB will continue executing its mobile-first strategy and to promote digital transformation of retail finance. The company will do this by building platforms, extending application scenarios, and traffic operations. It will also build a service system covering all products, channels, and customer groups to provide customers with the optimal experience.
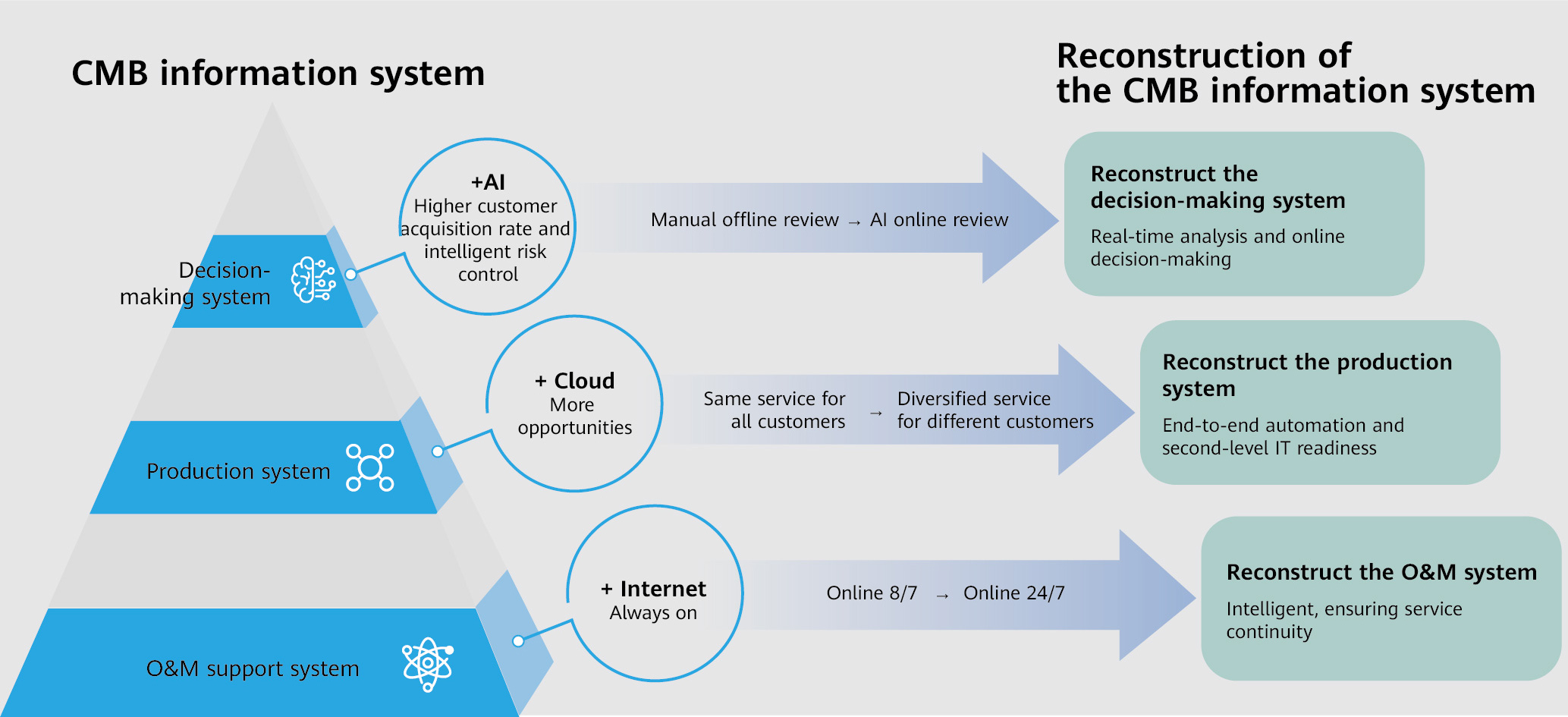
Figure 1: Reconstruction in three layers of CMB’s information system
The financial technology transformation centered on app operation requires transformation and planning in different areas. These include customer service, operation mode, and organization architecture using financial technologies. It also requires a vast transformation and reconstruction to IT infrastructure, which brings severe challenges to networks.
Firstly, in the decision-making system, real-time and intelligent requirements of services make big data analysis increasingly popular in the service chain. Prompt big data analysis is important. The Artificial Intelligence (AI) is related to both IT computing power and network performance. High throughput, low latency, and zero packet loss are basic requirements for networks. Traditional networks limit the improvement of AI training efficiency. Secondly, financial services require agility. However, with traditional operations, weekly delivery and daily network policy provisioning are far from agile. Thirdly, the O&M support system needs to ensure service continuity and enhance stability and visualization. The system also needs to provide an insight into the network and its data as it is interconnected, scaled-up, and made more complex due to increased traffic.
There are three main aspects that represent CMB’s digital transformation practices.
• Reconstructing the Decision-making System and Using Intelligent Lossless Ethernet to Achieve Efficient Running of AI Data Centers
Service intelligence can’t be achieved without big data. Today’s data center can better realize its potential than ever before. The data center contains service, customer, and O&M data, which is increasing explosively. What matters is how to use this data, and CMB has now diversified services, including intelligent customer service, smart marketing, and Machine Gene Investment. The data is continuously creating value for CMB. Meanwhile, real-time data analysis is gradually being adopted in CMB’s services. Prompt big data analysis is becoming increasingly important. For networks, big data analysis requires not only high bandwidth, but also low latency and zero packet loss capability.
CMB has implemented data analysis in the branch cloud, which is an innovative pilot of CMB’s cloud computing strategy, with the company adopting a deployment architecture with separated computing and storage. The IT system department of CMB has introduced the Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA) to improve the overall network throughput and reduce CPU consumption. This provides users with the same experience as accessing local disks. RDMA is a technology that is extremely sensitive to latency and packet loss, and according to the test data of CMB, approximately one thousandth of packet loss results in the loss of half of the network throughput. Therefore, zero packet loss is required on networks.
However, the Ethernet is a less reliable network in a traditional data center network. Fortunately, Huawei CloudFabric data center network provides CMB with an intelligent lossless Ethernet solution. With this solution, CMB has achieved high throughput, zero packet loss, and low latency by using iLossless, an intelligent lossless switching algorithm. According to the AI training test, the throughput of a compute node accessing a storage node in a 25GE NIC reaches 2.8 GByte/s. The throughput of the entire storage cluster is increased by at least 20 percent compared with that of a traditional network. This is equivalent to four to five iterations per second. Next, to propel the AI strategy, CMB is planning to introduce the intelligent lossless Ethernet to the Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) cluster with 300 NICs.
• Reconstructing the Production System and Building Full-Process Automation Through ADN Joint Innovation
The IT infrastructure of CMB increases exponentially with the digital transformation of financial services and the advancement of technology strategies. These include cloud computing, big data, and AI. From the beginning of 2017 to October 2018, the growth of CMB’s computing and network resources exceeded its inventory for the previous 10 years. The number of app visits has reached 450 million per day with the peak number reaching up to 15,000 per second.
The rapid growth poses significant challenges to the construction of infrastructure, with the service agility requiring frequent network changes. How can we build a full-process and automatic chain to efficiently implement service intents in network configurations? This is one of the biggest challenges that CMB has faced, and to find solutions to this, CMB and Huawei have made joint innovations and explorations.
In 2017, CMB deployed Huawei’s CloudFabric data center network in an availability zone with 2,000 nodes in the newly built Xili cloud data center. If a traditional deployment mode was used, it would take at least two weeks to complete the delivery, connection, and verification of the basic network of the same scale. However, using Huawei’s iMaster NCE and the Zero-Touch-Provisioning (ZTP) function, CMB implements automatic delivery of overlay configurations. Therefore, service configurations can be delivered in minutes, shortening the delivery of basic networks to three days. Overall, this greatly reduces the pressure in the resource delivery phase.
Although network resources are efficiently delivered, there will still be endless service rollout and auto scaling, and a huge gap exists between the service intent and the final network configuration. For example, network engineers often face the service requirement scenario where service growth is expected to exceed 50 percent. A network engineer may be unable to handle such service requirements, because 50 server nodes need to be added, 500 IP addresses need to be allocated, or even 5,000 network policies to be enabled. Although automation is implemented in parts of the work for the network engineers, full-process automation isn’t achieved. It’s estimated that capacity expansion of such scale takes approximately one month, with IT engineers facing high communication and rework costs caused by incorrect or missing configurations.
To address this pain point, CMB and Huawei launched a joint innovation project to discover breakthroughs and solutions and to achieve success in the Autonomous Driving Network (ADN). The project aims to identify business intents as network behavior and form a complete closed-loop of policy, verification, delivery, and verification. This can be implemented so that the overall network delivery time, and operation and capacity expansion time can be shortened to just days.
• Reconstructing the O&M System and iMaster NCE FabricInsight Achieving Quick Intelligent O&M
O&M usually goes through several phases, where the first phase is to ensure stability and service rollout, as changes may pose risks. Meanwhile, O&M engineers want to achieve high visualization, which means that indicators can be measured and visualized. In the second phase, it is impractical to avoid changes with the development of financial technologies and business needs more agile changes. In this phase, platform automation is the key. However, automation will also bring further problems, with the main challenge being that the network becomes a black box, and traditional O&M can’t meet the requirements. However, a massive amount of O&M data also drives intelligent O&M based on big data and AI, leading to the third phase of AIOps.
The CMB cloud data center introduced Huawei’s iMaster NCE FabricInsight network intelligent analyzer to implement automatic fault identification. The product was also designed to achieve intelligent fault locating, and potential risk prediction based on big data and AI algorithms. The major difference between FabricInsight and the traditional O&M is that FabricInsight manages the entire network from the service perspective. Each network device is a probe on the network and can perform full-path O&M management for each service flow. This allows for implementation of fault identification within one minute, fault locating within three minutes, and fault rectification within five minutes.
In July 2018, shortly after FabricInsight went online in the data center of CMB, CMB service personnel discovered a significant number of retransmission alarms were generated between the big data cluster and Kafka cluster of a channel. It was estimated there were 300,000 alarms per hour, but it wasn’t possible to instantly determine the cause of the alarms. Nevertheless, the root cause was quickly found with FabricInsight’s intelligent analysis. A port of a server in the Kafka cluster responded slowly to syn.ack, causing a vast number of retransmission alarms. Only several minutes were needed to locate the fault’s root cause, and after the network engineer notified the service department of the cause it was confirmed by the service department. The fault was then rectified after the application was restarted.
In the traditional O&M process, service personnel have found that access is slow and the cause can’t be found, so they have to call the network engineers and ask them to check the network. It usually takes a long time for network engineers to locate faults, which negatively impacts services. As a result, complaints frequently come from the business department about the network department. In the past, the network wasn’t transparent and there have been numerous unclear situations. In contrast, FabricInsight makes networks more visual, which equips network O&M engineers with a greater insight into networks. CMB also has high expectations for FabricInsight, hoping to further improve intelligent functions, including intelligent prediction and automatic verification of changes. Overall, this will help CMB advance toward the ADN.
Huawei’s CloudFabric data center network provides powerful support for CMB in digital transformation and digital operation reconstruction. Huawei will continue to partner with CMB to promote Retail Finance 3.0 and shape the future of financial AI.

Figure 2: Huawei’s CloudFabric builds the best data center network for financial digital transformation

China Merchants Bank (CMB) was founded in 1987 in Shenzhen, the city at the forefront of the reform and opening-up of China. It is the first share-holding commercial bank to be wholly owned by corporate legal entities in China. Over the past 30 years, CMB has developed rapidly and was ranked No. 188 in the Fortune Global 500 list in 2019. Among the Top 1000 World Banks list in 2018 released by The Banker, CMB was ranked No. 1 by business performance indicators among all banks in China.