Produits, solutions et services pour les entreprises
Akıllı Telefonlar, Bilgisayar&Tabletler, Giyilebilirler ve Daha Fazlası
Today, we are seeing explosive growth in data elements, and computing power demands are increasing exponentially. However, traditional network architecture remains like a one-way country backroad. Our cities need multi-lane highways if they hope to carry the traffic of smart cities. Choppy video streaming, vehicle-road synergy hindered by lag, and isolated computing silos all remind us that for our cities to be smarter, optical network connections themselves need to first become smart.
F5G-A is a technology that can address this issue, as it can connect data and computing power and pave the way for truly smart cities.
Data has emerged as a new factor of production and a driving force behind economic growth. In response, China's National Data Administration has decided to reform the country's market-based allocation system for data elements. Their aim is to turbocharge the evolution of city networks, so that they can provide not only traditional connections and IoT, but digital and intelligent connectivity based on all-optical connections.
Digital connectivity refers to connections between data elements. These connections accelerate the large-scale, efficient, and reliable flow and utilization of data across different levels, regions, systems, departments, and businesses. This streamlines the process of data supply, transfer, and utilization.
Intelligent connectivity, on the other hand, refers to the connections of intelligence and computing power. These connections form a network that interconnects massive amounts of data, efficient computing resources, and intelligent services, so that every person, home, and organization can benefit from intelligence.
Finally, all-optical connectivity mainly refers to the connections that make up a city's optical network, which is the foundational infrastructure that powers smart cities. Both digital and intelligent connectivity rely on optical connections, which makes optical networks as important as traditional infrastructure, like water, electricity, gas, and roadways. In fact, communications networks can be considered the fifth layer of critical infrastructure in a city, as they serve the digital economy, digital government, and digital society.
A city's all-optical infrastructure is its optical network, which is based on fiber transmission functions. Urban optical networks serve as the foundation of new information infrastructure, so they must be able to transmit massive amounts of data and meet the requirements of a wide array of upper-layer applications (see Figure 2).
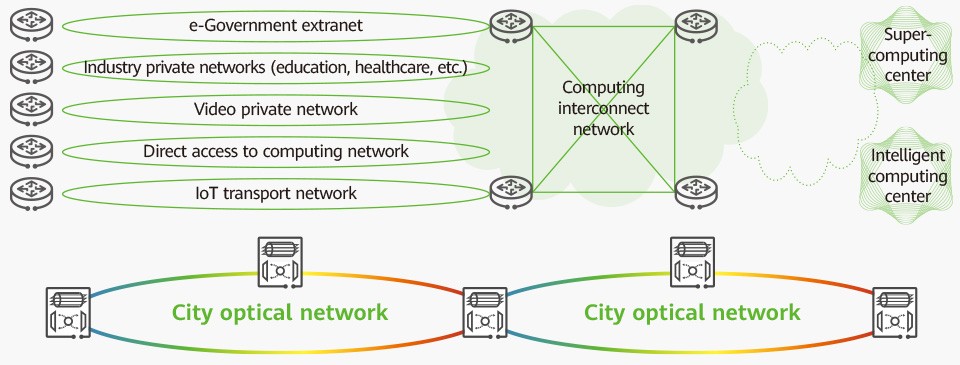
Figure 2: One city optical network foundation + N service networks
F5G-A comes with a number of core capabilities that are needed to build a solid foundation for smart cities, including ultra-high bandwidth, ultra-low latency, ultra-high reliability, ultra-high security, energy saving technologies, intelligent O&M, and advanced quality assurance. F5G-A has already demonstrated its immense value in many fields, such as private network integration for digital government, foundation model training for city governance, video private network upgrade, vehicle-road-cloud synergy, computing private network construction, and digital twin construction. At the same time, it plays a significant role in digital and intelligent connectivity.
First, for digital connectivity, F5G-A optical networks are able to support secure and reliable data element flow.
To unleash the value of different data elements, data sources must be accurately identifiable, data flows must be secure and reliable, and data platforms need to be able to efficiently store, analyze, and apply data.
Security and trustworthiness: Different data elements often contain a large amount of sensitive information, including confidential business secrets, so networks must be highly secure to ensure secure and reliable data flow. Hard pipe–based optical networks can ensure the physical isolation of different types of service data. In addition, these networks can use the AES256 algorithm or quantum encryption to separate plaintext data from ciphertext data for transmission, further improving data security.
Ultra-high bandwidth: There are many types of data elements, and many elements are unstructured data such as video. These types of data require higher bandwidths to transmit. As IoT technologies become more widely used, devices and sensors will continuously generate larger and larger amounts of data. Enterprise services will produce foundation model data and research institutes will produce explosive amounts of experimental data. F5G-A optical networks provide the ultra-high bandwidth needed to ensure efficient data flow for these elements.
Second, for intelligent connectivity, F5G-A optical networks allow computing centers to efficiently collaborate thanks to their ability to provide 1 ms latency circles (with access to computing power) in cities.
Many new service scenarios are emerging thanks to this efficient access to computing power, including multimodal AI interaction, intelligent computing training, and device-cloud synergy. A future-oriented premium network is required to unleash the value of this computing power. The high bandwidth, low latency, and high reliability of optical networks are ideal for efficient interconnection of computing power, which then further enhances computing with fiber and drives computing with fiber.
AI and general-purpose computing power are also expected to see rapid growth in the near future, which will put even higher requirements on network bandwidth. By 2030, AI computing power is expected to increase 500-fold and general-purpose computing power 10-fold. This means city networks will need to be able to provide at least 100 Gbps bandwidths. Ultra-broadband optical networking enables a single optical fiber to carry over 100 Tbps of bandwidth, which is more than enough to handle these computing power surges and ensure efficient data flow.
Ultra-low latency: Latency is a key factor for applications that require high real-time performance, such as autonomous driving in smart transportation and real-time control in industrial automation. Computing power needs to quickly respond to input data and output results in a timely manner. A high-latency network slows down system responses, which can affect the security and reliability of many applications. Again, city optical networks can provide a 1 ms intra-city latency circle, which ensures ultra-low latency for computing power.
Ultra-high reliability: Applications like foundation model training and inference, local storage + remote computing power, and computing power collaboration have high data accuracy and continuity requirements. A faulty or interruption-prone network will affect services and cause computing power performance deterioration. City optical networks with ultra-high reliability can guarantee stable connection and long-term stability thanks to their multi-level redundancy features and real-time network monitoring.
Intelligent and digital connectivity, in the context of city networks, relies on optical network infrastructure. This makes optical connections a must for smart cities. Governments everywhere need to begin thinking about building their own F5G-A optical networks to streamline urban data flows and computing power connection. This will be the only way to ensure secure, reliable, and efficient operations and drive the continuous evolution of smart cities.
Source: HuaweiTech
Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the official policy, position, products, and technologies of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. If you need to learn more about the products and technologies of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd., please visit our product pages or contact us.