This site uses cookies. By continuing to browse the site you are agreeing to our use of cookies. Read our privacy policy>
![]()
This site uses cookies. By continuing to browse the site you are agreeing to our use of cookies. Read our privacy policy>
![]()
Enterprise products, solutions & services
The widespread application of new ICT technologies, such as cloud, big data, the Internet of Things (IoT), and mobile Internet, has promoted the digital transformation of various industries but also brought many security risks and challenges. In recent years, vicious security events have emerged one after another, such as external APT attacks and large-scale data leakage caused by internal violations. Information security owners of organizations have gradually realized that traditional border protection methods have many limitations and cannot meet network security requirements in the new situation.
First, with the continuous extension of network edges and wide deployment of hybrid network environments covering cloud and on-premises services, enterprise network architectures are increasingly complex, while security products and tools still cannot collaborate with one another. Second, new technologies and applications provide new carriers for network attacks, which thereby become more flexible, covert, and intelligent. The attacks span networks, applications, contents, and devices, making threat detection and source tracing more difficult. Finally, with the digital transformation trend in various industries, data sharing and circulation are becoming rigid service requirements. Isolated service networks will be converged, and security boundaries will be broken, further increasing security control difficulties and information leakage risks.
According to Gartner's survey, 75% of enterprise organizations are actively seeking comprehensive integration from security suppliers; inefficient operations and inability to effectively tackle challenges on integration of heterogeneous security architectures continue to raise concerns among security and risk management leaders, who are in urgent need of more efficient and fully integrated solutions that can replace the isolated single-point security products.
To cope with these challenges and reconstruct security from the perspective of the new IT architecture, Huawei provides unified security resource and capability management as well as unified policy configuration for clouds, networks, edges, and endpoints. The aim is to achieve unified orchestration of security service chains, network-security integration based on SASE, unified zero trust capabilities, and unified analysis of and response to multi-dimensional events. Then a unified and complete "cloud-network-edge-endpoint" security system is built. This is an active exploration for building network security defense lines in the digital era.
As shown in Figure 1, the "cloud-network-edge-endpoint" security system contains a series of security resources and capabilities deployed on clouds, networks, edges, and endpoints. Specifically:
• Cloud: involves SaaS-based security cloud services designed for public cloud tenants and traditional non-public cloud users.
• Network: involves security resources deployed on traditional WANs, campus networks, data center networks (DCNs), and branch networks.
• Edge: involves security gateways or edge security resource pools that are close to end users.
• Endpoint: involves security capabilities deployed on user endpoints or servers.
Figure 1 Unified management, intelligent analysis, and automatic response, building a unified "cloud-network-edge-endpoint" security protection system
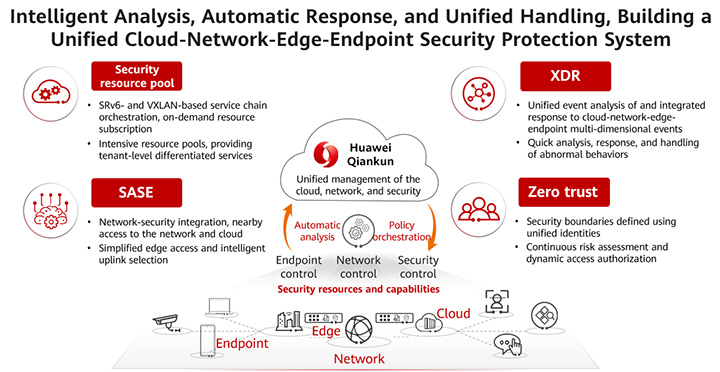
Centralized management is the core capability of the unified "cloud-network-edge-endpoint" security system. Huawei Qiankun's cloud-network-security integrated controller integrates cloud-network-edge-endpoint security resources and capabilities into a unified security solution — an easy-to-use automatic security protection solution that extends from enterprise campuses and private data centers to networks, clouds, and remote offices.
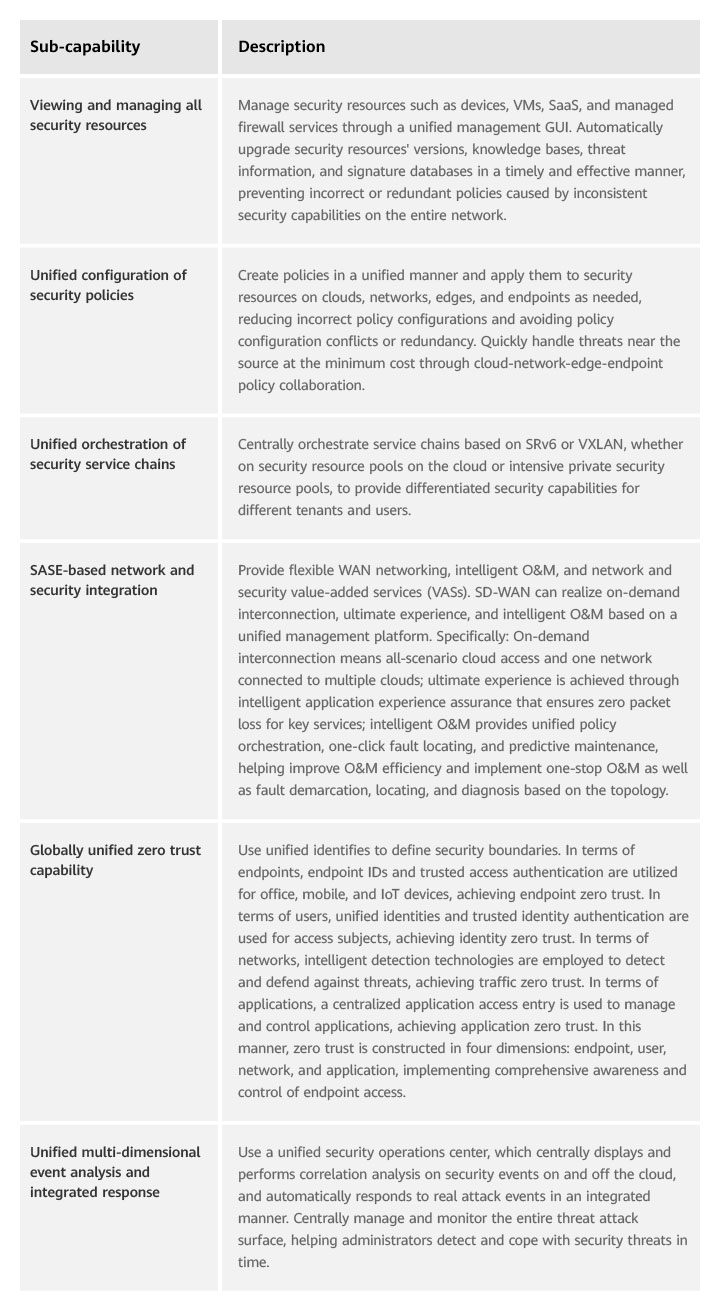
Table 1 lists the sub-capabilities supported by centralized management.
Table 1 Centralized management sub-capabilities
Take the security gateway as an example. To implement centralized management, the Huawei security gateway platform integrates the cloud-network-edge security capabilities. As shown in Figure 2, the layered architecture of security services and network services adapts to different underlying platforms and evolves into multiple forms of security gateway resources, such as embedded security gateways, virtualized and cloud-native firewalls, and firewall as a service (FWaaS). Based on the same set of code, the same capabilities can not only integrate a large amount of security resources into a simplified single policy and management framework, but also ensure various security resources can be configured in a unified manner and are interoperable.
Figure 2 Layered security services and network services adapting to different underlying platforms and evolving into multiple forms of security gateway resources
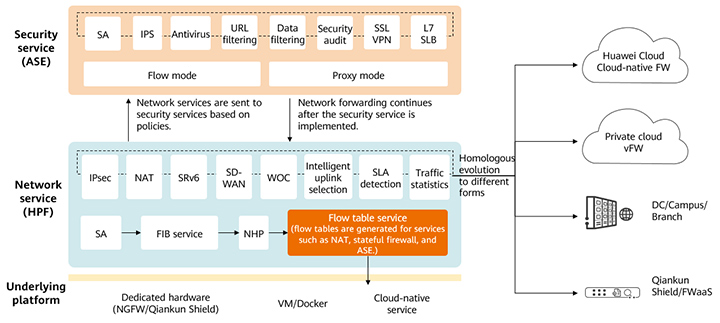
The following describes how Huawei uses the layered service architecture to evolve the same set of code into multiple forms of security gateway resources.
Security service Adaptive Security Engine (ASE): processes security services from L4 to L7 and supports advanced security capabilities, such as application protocol identification, IPS, antivirus, data filtering, and L7 SLB.
Network service High Performance Forward (HPF): forwards network services and processes transport-layer services from L2 to L4 (partial L4 services), such as SRv6, SD-WAN, NAT, WOC, and tunnel services. The flow table service is the forwarding plug-in of the firewall policy and is responsible for quickly processing the service status of the security flow table.
Underlying platform adaptation: supports dedicated hardware (embedded) and common VMs or Docker platforms, and allows direct invocation of cloud-native services to start security services. If an underlying platform has the hardware acceleration capability, the flow table service of the network service can be delivered to the platform to improve the corresponding processing performance.
Dynamic resource allocation: supports dynamic resource adjustment between containers in different scenarios. For example, the network service HPF is allocated more compute resources in SD-WAN-focused scenarios, and the security service ASE is allocated more compute resources in advanced security-focused scenarios.
This architecture supports multiple security scenarios, such as campus, data center, cloud-native security, and SD-WAN, and allows flexible resource allocation based on scenarios, improving security performance and reliability while reducing O&M costs.
Huawei's unified "cloud-network-edge-endpoint" security system proposes the concept of integrated management, analysis, decision-making, and handling. It transformed the traditional single-device, static, and passive security protection roadmap and builds an intelligent network security architecture, to implement real-time risk detection, proactive threat analysis, and intelligent global prevention and control.
Integrated management: uses a unified management platform to centrally manage all security resources and capabilities, improving security management efficiency.
Security policies are formulated in a unified manner and delivered as needed to ensure the consistency and effectiveness of all security policies. This reduces network security O&M and management costs and improves enterprises' return on investment (ROI).
Integrated analysis: comprehensively collects multi-dimensional threat data from clouds, networks, and endpoints and collaborates on- and off-cloud data, improving threat analysis accuracy and displaying security posture in all domains in a unified manner.
To improve the accuracy of security event analysis, information needs to be collected as much as possible, especially endpoint (including servers) risk information, network traffic information, and security device logs. Such information is scattered at different network locations. Therefore, unified "cloud-network-edge-endpoint" management is a must, with a unique security operations center deployed, to obtain more accurate analysis results.
Integrated decision-making: makes decisions and dynamically adjusts authorization or security policies in real time based on multi-dimensional risk data such as endpoint, network, and user behavior data as well as information such as locations, users, and time.
Core resources are secured to the fullest extent possible. After the first authentication succeeds, risks of endpoints and users need to be evaluated in real time from dimensions such as endpoint risk, network traffic exception, and user violation (for example, sudden change of the access location). Based on the evaluation results, the system scores the risks of the endpoints or users, adjusts their rights based on identities, and performs operations such as degradation and blocking.
Integrated handling: implements global "cloud-network-edge-endpoint" attack source tracing and selects the most appropriate method and security resources closest to the attack source for automatic handling.
Once a serious threat is identified, it must be confirmed immediately and contained to avoid further spread. Through automatic collaboration between devices, threat sources are quickly located within minutes and handled within seconds.
Distinct from traditional single-point protection, Huawei's unified "cloud-network-edge-endpoint" security system integrates security capabilities into clouds, networks, edges, endpoints, and service systems. By addressing security issues from a service system perspective, it empowers customers to tackle increasingly complex and ever-changing attacks. Additionally, the system ensures service resilience, in response to the disappearance of traditional security boundaries and constant expansion of network edges.
Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the official policy, position, products, and technologies of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. If you need to learn more about the products and technologies of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd., please visit our website at e.huawei.com or contact us.