Intelligent IP Network Leads WAN into the All-Service Intelligence Era
This site uses cookies. By continuing to browse the site you are agreeing to our use of cookies. Read our privacy policy>
![]()
Продукты, решения и услуги для предприятий
Смартфоны, ПК и планшеты, носимые устройства и многое другое

In the digital wave, a wide variety of industries are accelerating digital exploration and transformation. For enterprises, the core of digital transformation is to reshape business models, service processes, and organizational structures so that all services can be driven by data, improving the customer experience and organizational efficiency while driving business growth. The ultimate goal of enterprise digital transformation is to bring digital immersion to enterprises and enable data flows within enterprises.
All technologies that support enterprise digital transformation, such as cloud and Internet of Things (IoT), are network-centric in nature. This means that networks, especially Wide Area Networks (WANs), have a direct impact on the success of digital transformation. For example, during digital transformation of the electric power industry, remote detection and control of power production services are required, making the network that carries the data for detection and control indispensable. Any deterioration in network quality may affect production monitoring and even lead to production accidents. In this context, WANs are the foundation for enterprise digital transformation. Throughout the digital transformation journey, WANs have experienced three eras: office interconnect, private service network, and all-service intelligence.
The first generation, which started in 2000, is known as the office interconnect era. This era saw the emergence of tools such as Word and Excel, making statistics collection possible for office services. These tools, together with word processing, signaled the transformation of offices from paper to digital information. During this phase, the bandwidth requirements on WANs were low, and E1, STM-1, and FE physical interfaces were primarily used. Service experience could be met as long as the network was reachable, with low SLA requirements. Also, network O&M was mainly command-driven.
The second generation, which started in 2010, is known as the private service network era. ICT gradually entered the production system of enterprises, generating multiple independent private networks for production, office, and other purposes. SDH networks were mainly used for production, which required high-quality transport. The growing need for centralized management and control and the emergence of video services pushed office networks to evolve towards higher bandwidth. Physical interfaces were mainly GE, 2.5G, and 10GE interfaces. Still, SLA requirements were not high, and service quality could be guaranteed through simple QoS. In terms of O&M, simple tools were used to implement preliminary automation.
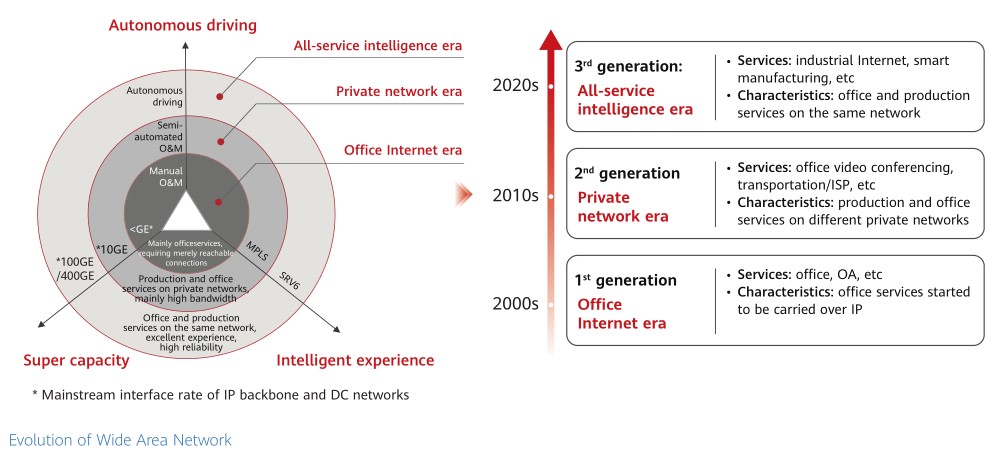
The third generation, which started in 2020, is called the all-service intelligence era. Oriented toward services such as industrial Internet, IoT, and cloud, ICT has become the core production system of enterprises and requires the consolidation of data from diverse fields (such as R&D, manufacturing, finance, and marketing) for big data analytics and collaboration. The production, decision making, and operation of enterprises are driven by various data. Enterprises require network convergence and big data interworking, and therefore, all services need to intelligently run on one WAN.
Challenge of bandwidth: In terms of network access, extensive interfaces must be available to support production services for all-service transport. Such interfaces include E1, POS, and PCM interfaces for the electric power industry and E1 and POS interfaces for the financial industry. In terms of traffic, high-bandwidth services, such as video conferencing, are gaining popularity. Taking 4K video conferencing as an example, a video conference with 20 parties requires a stable bandwidth of about 100 Mbps.
Challenge of service experience assurance: The trend of carrying all services on one network is making experience guarantee, such as latency guarantee, a must-have for production services. Take the financial industry as an example. Services, such as online transactions, require a stable latency. If a stable latency cannot be provided, the transaction may be delayed or even fail.
Challenge of intelligent experience: As the network scale expands and services are migrated to the cloud, automated network deployment, fast fault locating, and intelligent traffic optimization have become increasingly important. Take fault locating as an example. On a large-scale OTT network, services pass through 32 network nodes on average from users to the data center and may traverse thousands of paths, making it difficult to visualize service quality. Network fault locating takes days or even weeks.
To meet the requirements of the all-service intelligence era, Huawei has developed the intelligent IP WAN solution based on years of innovation and industry experience. The intelligent IP WAN solution uses NetEngine series intelligent routers to offer super capacity and support all-scenario coverage and on-demand service access. The solution also uses FlexE-based network slicing to guarantee and flexibly allocate bandwidth for critical services, allowing one network to carry both office and production services. SRv6 is used to ensure committed latency, build intelligent connectivity, and support optimal experience for all services. iMaster NCE — the industry’s first intelligent O&M platform that features integrated management, control, and analysis — is used to implement full-lifecycle intelligent O&M and support automated service provisioning, minute-level fault locating, and predictive O&M.
Super Capacity: Most Comprehensive Interfaces, with FlexE-Based Slicing for Flexible Bandwidth Adjustment
Based on NetEngine series products, Huawei’s intelligent IP WAN solution supports the most comprehensive interfaces on a single device and applies to both the production and office scenarios. Huawei NetEngine series routers support PCM, E1, SDH, GE, and 10GE interfaces as well as 100GE and 400GE network-side interfaces, meeting the requirements for extensive interfaces and high bandwidth of enterprise services. At the aggregation and core layers, the cost-effective 400GE will become the next-generation networking technology following 100GE. Oriented to the 400GE networking era, Huawei launched the industry’s first E2E 400GE solution (from aggregation to core and backbone) to meet the needs of the massive traffic growth that is projected for the future. Huawei is the major contributor to 400GE standardization and the industry’s only vendor that can provide full-distance 400GE optical modules covering transmission distances over 10, 40, and 80 km. Huawei helped a carrier deploy the industry’s first commercial 400GE network in February 2019.
In the same way that traffic congestion may occur regardless of how wide a road is, the traditional IP network may fail to guarantee the bandwidth of critical services (such as production services) even if the network capacity is high. This is because all services share bandwidth resources and preempt each other in case of traffic bursts. Huawei is the first in the industry to propose and develop FlexE-based network slicing, which is similar to a dedicated lane on the road — it implements hard bandwidth isolation between different service traffic on the ultra-broadband network. This solution provides 100 percent committed bandwidth for services, such as enterprises’ production services. The slice bandwidth can be flexibly adjusted to adapt to service changes. Huawei’s FlexE-based network slicing technology is also five times more fine-grained than the industry average, supporting more production services and finer bandwidth scheduling.
Intelligent Experience: Committed Latency and Optimal Service Experience
Oriented toward the converged transport of office and production services, Huawei’s intelligent IP WAN solution provides SRv6-based latency commitment to ensure the experience of critical services, such as production services. On a traditional IP network, service paths are uncontrollable, and the latency can’t be guaranteed. Huawei is the first enterprise in the industry to support SRv6-based intelligent traffic steering. SRv6 allows the optical path to be selected in accordance with service latency requirements, ensuring low latency of critical services, such as production services.
The intelligent IP WAN solution uses SRv6 to speed up service provisioning, implement cloud-network synergy and one-hop access to the cloud, allow service provisioning within minutes, and support 50 ms protection switching in 100 percent of all topology-independent scenarios, ensuring high service reliability. Huawei is committed to promoting the development and large-scale commercial use of SRv6. As the largest contributor to SRv6 standards, Huawei has participated in the formulation of more than 59 percent of SRv6 standards. To date, SRv6 has been commercially deployed by more than 20 carriers worldwide.
Autonomous Driving: Full-Lifecycle Intelligent O&M, Moving Toward Autonomous Driving
With iMaster NCE — the industry’s first intelligent O&M platform that integrates management, control, and analysis — Huawei helps customers achieve automated and intelligent O&M throughout the entire lifecycle. iMaster NCE implements centralized coordination and orchestration as well as automated service configuration across network layers and vendors, enabling minute-level E2E service provisioning. Based on big data analytics, iMaster NCE supports visualized and manageable network quality as well as minute-level fault demarcation and locating. Fault locating is a prime example. Huawei is the first in the industry to propose the iFIT technology to implement performance detection per service and per flow, supporting SLA visualization. The combined use of iMaster NCE and iFIT allows fault locating within minutes and ensures high network reliability. Huawei’s iFIT won the Best of Show Award Special Prize at Interop Tokyo 2019. To date, iMaster NCE has been put into commercial use on more than 80 networks worldwide, helping customers implement intelligent WANs.
Huawei’s intelligent IP WAN solution helps customers build WANs featuring vast capacity, intelligent experience, and autonomous driving — leading WANs into the all-service intelligence era and helping enterprises grow with speed, agility, and efficiency in the digital wave.