What Do CXOs Want From Digital Transformation?
This site uses cookies. By continuing to browse the site you are agreeing to our use of cookies. Read our privacy policy>
![]()
Enterprise products, solutions & services

Emerging digital platforms are changing business models around the world. Over the past decade or so, Internet and tech giants like Google, Apple, Amazon, Facebook, Microsoft, Uber, and Airbnb have found unprecedented success, and they all started with a cloud. A common characteristic among these companies is that they all utilize the platform model and strive to develop new Information and Communications Technology (ICT).
Inspired by the accomplishments of these industry giants, traditional mainstream industries are increasingly aware of the business value that common platforms can generate. At Huawei, we are both a witness to and partner in the success of many leading companies throughout the automotive, consumer electronics, finance, and energy industries. Huawei provides support and collaboration to many visionary firms that are committed to building their own specialized platforms, such as PSA Peugeot Citroën for automobile networking, The Walt Disney Company’s MagicBand, Nike+, ABB Ability, Siemens’ MindSphere, Philips’ HealthSuite, and Haier’s COSMOPlat.
So, what kind of platforms do enterprises wish for as they go digital? How should they select a platform supplier? And what expectations do they have for the current generation of digital platforms and platform suppliers? CXOs from Ping An, Goldcard, Shenzhen University, and CERNET shared their thoughts on this matter with ICT Insights.
► Ping An Group Finds Value in Digital Transformation
► Goldcard: Digital Transformation Ignites Public Utility Potential
► Shenzhen University: A New Smart Campus Experience
► Building the CERNET Digital Education Platform

Ping An Group (Ping An) is a financial services company that is active in many vertical markets, including health care and Smart City planning, and despite the company’s current wide-range, remains focused on its core expertise in the digital transformation of the financial technology sector. Ping An has encountered two main challenges in the area of digital transformation.
First, the development of the digital economy is spurring transformations across every industry, yet the value of the results is still being determined. How is it that new digital solutions, such as AI + Big data + Cloud (ABC) platforms, improve business value and help companies leverage change? However challenging, a key step to joining the digital economy is to find methods to apply these new technologies in seamless, efficient, and green ways.
Second, as the digital economy continues to evolve rapidly, engineers are inspired to create new and better ICT solutions to address previously unforeseen scenarios. In all cases, innovation comes with information security, management, and technical risks — and especially in the area of information security, mitigating risk when adopting new technologies is a threshold challenge before any enterprise can embrace the full potential of the digital age.
• Digital Transformations Require Mature Digital Platforms
We believe that mature digital platforms are an essential resource to the successful fulfillment of the digital transformation process. This is true not only for enterprises, but also for nations. In the era of the digital economy, China’s national cybersecurity and information services depend on the support of advanced digital platform technologies. Leading enterprises across all industries in China — including Ping An in financial services; Huawei in telecommunications; and Haier, Midea, and Gree in home appliances — all require mature digital platforms to carry out their large-scale transformations.
The development of any enterprise is dependent on the adoption of new technologies, and the bigger the enterprise, the more technical resources it needs:
• Future Smart Office — Transitioning from traditional paper-based offices to paperless smart offices improves efficiency and reduces emissions.
• Full connectivity, mass data storage, in-depth data analysis, and precision marketing — These features help companies shift from traditional, quantity-driven development models to a form of enterprise development where quantity and quality are equally important.
• Cloud computing — The Chinese government is encouraging enterprises like Ping An, Huawei, China Merchants Bank, and Hainan Airlines to adopt cloud computing. Cloudification has become a rigid demand for enterprise development in order to meet national development requirements.
All of these innovations are dependent on digital platforms and digital technologies like AI, big data, and cloud infrastructure.

Huawei and Ping An are strategic partners. The two companies have a long history of extensive cooperation that is focused on data centers and ICT infrastructure, including network equipment, servers, and the specifications for equipment room construction. Information security, in particular, has become increasingly important as Ping An’s business has grown. The two companies continue to have in-depth discussions about how Huawei’s next-generation firewalls, border defense equipment, AI security, big data security analytics, and other platform technologies can keep up with Ping An’s application and technical needs. Ping An’s financial services business has already deployed many of these technologies. Additionally, Huawei is an important strategic partner in the Smart City market, an area where Ping An continues to expand its work.
As part of this collaboration, Huawei provides two important strengths. The first is specialization in the development of digital platforms and technologies, through which China’s national industries have received help as a result of Huawei’s continuous investment in R&D and commitment to an independent R&D model. The second is Huawei’s specialist teams. Digital platform specialists support their customer base by helping enterprises implement automation, intelligence, and visualization applications through continuous optimization and evolutionary processes.
• Building a Favorable Industry Ecosystem For the Digital Platform
Huawei strives to create digital platforms, train employees, and continuously launch excellent products and solutions. Looking into the future, the company is acting as a ‘guiding intermediate force’ to build ecosystems that help companies like Ping An better apply digital platform technology. This level of work will help entire industries realize their digital transformation goals.
Based on its experience working with Huawei, Ping An is building a digital ecosystem that supports its expansion into sectors beyond the finance industry. All enterprises need a similarly favorable industry-development environment.
The Ping An Group hopes Huawei will continue to contribute to building digital platform ecosystems by providing key specialists, and that they share their experience with the entire financial technology industry, particularly on the topic of constructing AI platforms. This type of cooperation is helping the whole industry to use digital platforms to their maximum potential. In this regard, Ping An plans to work together with Huawei to quickly fuel the development of digital ecosystems for multiple industries.

Founded in 1997, Goldcard Smart Group Co., Ltd. is a complete public utilities-solutions service provider that offers continuous innovation based on customer requirements. Goldcard solutions cover smart devices, communication networks, application management, and Internet cloud services. Listed on the Shenzhen Stock Exchange since 2012, the company serves over 2,000 public utility enterprises and more than 35 million households in over 1,500 cities.
Goldcard has been exploring and implementing natural gas Internet of Things (IoT) solutions since 2013 — including the world’s first Narrow Band-IoT (NB-IoT) proof-of-concept project for smart meter reading, and has been committed to promoting the development of smart utilities worldwide. To date, Goldcard has installed more than 5 million IoT meters across China. The company has also begun early trials for cloud-based, back-end data processing and business support. Today, Goldcard boasts over 500 public cloud customers and more than 1.5 million IoT devices connected to the public cloud.
As a pioneer in IoT applications in China, Goldcard has encountered numerous difficulties and challenges during implementation. On the device side, the company has adapted smart meters to low-power, low-cost applications and reduced their dependence on the network. On the cloud side, Goldcard has invested countless resources to innovate device connection management; process the massive quantities of data generated and collected by smart meters; eliminate performance bottlenecks; and minimize security risks.
The use of digital platform technologies, such as the IoT and big data, has helped Goldcard reduce the cost of reading gas meters, enhance meter-reading accuracy, and increase its understanding of user needs. Digital platforms have strengthened the company’s ability to comprehensively forecast gas-pipeline network operations, and, in particular, the emergence of NB-IoT has been good news for smart gas applications. In terms of devices, the NB-IoT’s wide range of connections, low cost, and low power consumption are perfectly suited to gas meter reading applications. Huawei’s OceanConnect IoT public cloud platform provides many powerful tools for connecting, managing, and securing IoT devices. Application developers can access these tools to build complex upper-layer services that create value for consumers and provide a solid foundation for the digital transformation of gas and utilities.
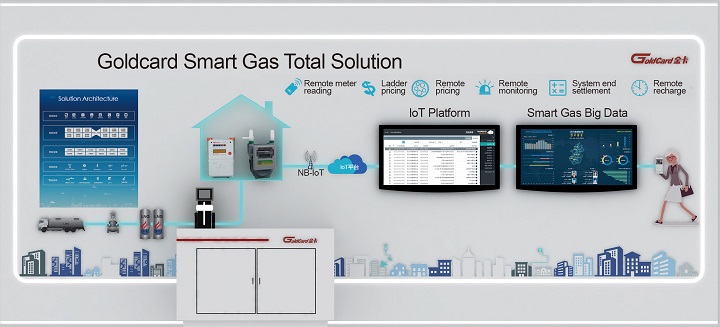
As the gas industry transforms digitally, it is essential that Goldcard has a mature platform to provide support. First, it is difficult for any single company or sector to harness digital platform applications, such as the IoT and big data, in a comprehensive or successful way. Enterprises need to cooperate with at least one powerful ecosystem partner. Second, Goldcard hopes to use the successful implementation of smart gas solutions as an entrée into other sectors — for instance, into security alerts for smart homes. This would also require the involvement of other device partners to create new sources of value through multi-dimensional, cross-sector integration, such as with cloud data platforms. Besides this, Goldcard has been expanding into overseas markets for the past two years, and hopes to bring its smart gas meter reading solutions to the rest of the world. Huawei is helping to promote Goldcard products globally, especially in countries along China’s ‘Belt and Road Initiative.’
Huawei offers mature digital platform technologies and has been committed to ecosystem construction for many years. Over the past four years, Goldcard has received valuable assistance from Huawei — including technical support, a deep understanding of the service provider’s needs, and a range of cooperative business models. Huawei has also diligently worked to certify Goldcard’s end products and complete solutions, especially in terms of safety and performance.
Goldcard believes Huawei digital platforms provide excellent functionality, and in the future hopes relevant vertical industry experts from Huawei, such as in the smart home connectivity field will communicate with the company to better understand its needs. Relevant teams within Goldcard have already made technical preparations in the area of big data applications, though in terms of business models, the company needs to further explore how to create new value, improve business practices, and find success stories that serve as reference cases. Huawei has extensive cross-industry experience and can help provide council in this area. When it comes to cross-sector expansion, the IoT is borderless. With the help of Huawei’s platform and ecosystem partners, Goldcard hopes to extend into other domains — from smart gas to smart homes, smart cities, and more.

Shenzhen University (SZU), originally founded in 1983, is also known as the ‘Special Economic Zone University,’ ‘Window University,’ and ‘Experimental University.’ Over the past 36 years, SZU has garnered recognition from around the world, and boasts a list of alumni that includes business leaders Ma Huateng (Tencent Holdings Limited), Zhou Haijiang (Hongdou Group Co., Ltd.), and Shi Yuzhu (Giant Interactive Group).
SZU has always attached great importance to technology-driven innovation and is committed to becoming one of China’s ‘Double First-Class’ universities that supports student-centered teaching methods through the use of technologies like cloud computing, big data, and artificial intelligence.
The goal of SZU’s smart campus is to build a modern university that satisfies the teaching, research, and social needs of both teachers and students.
• Smart Campuses Improve Management Efficiency and Safety
Since the turn of the century, SZU has responded positively to China’s national call to build ‘universities without walls.’ However, with the growing popularity of e-Commerce and delivery services throughout the country, innumerable package and freight deliveries enter and leave the campus on a daily basis. Campus security needs to be assured in the face of this free flow of people and vehicles, and manned security stations, alone, have been insufficient. So, SZU decided to improve its safety protocol by combining staffed checkpoints with cutting-edge technology.
In 2016, SZU installed the Huawei Smart Campus solution during the construction of its new Xili Campus. The university deployed 740 high-definition cameras supported on the back-end by an intelligent license-plate recognition system that monitors the flow of cars and trucks on campus; and a third-party face recognition platform that identifies students, staff, and visitors entering and leaving dormitories, buildings, and laboratories.
The Huawei Smart Campus technology has greatly improved security and safety at SZU. For example, theft rates have been reduced, which were previously common in public places, such as libraries and restaurants. And campus administrators are now able to direct emergency operations from a central monitoring room — like during typhoon Mangosteen in 2018 when a tree fell across a roadway and the exterior stairs of a building were damaged. For both situations, emergency personnel were dispatched immediately to the exact locations to assess the damage and begin repairs.
Smart Campuses allow people, cars, and physical facilities to be managed intelligently, which in turn makes administration more efficient and the environment safer. Centralized management reduces the need for manpower while enhancing security.

• Digital Platforms Create Crucial Infrastructure for Teaching and Research
With the completion of the Xili Campus, SZU began to operate three campuses across more than 10 kilometers; for which a Huawei-provided optical transmission network was used as a guaranteed, high-bandwidth Local Area Network (LAN) to interconnect the three campuses.
Huawei was also commissioned to build a first-class data center on the Xili Campus to support the expected reductions in cost from improvements in the efficiency of operations and maintenance. The result is a crucial component of SZU’s information infrastructure that is designed to provide continuous, long-term support for the school’s future.
The Huawei ICT platform includes an agile network; data center servers and storage; and on-campus, modular equipment rooms. Interactive classrooms incorporate smart recording systems that track teacher and student interactions and automatically turn lessons into video courseware. The Huawei Smart Campus solution provides SZU with an advanced environment for teaching, research, and the entrepreneurial development of teachers and students, allowing each group to focus on its respective endeavors more easily.
Huawei is leading the way in the global ICT industry — and because the company’s headquarters are also in Shenzhen, SZU enjoys extraordinary after-sales service. Altogether, there are many reasons SZU selected Huawei to build its Smart Campus. In terms of stability and security, the Huawei solution has performed exceptionally well; and continues to meet the university’s needs for teaching, research, and campus life. SZU looks forward to greater cooperation with Huawei in the future.

The China Education and Research Network (CERNET) is one of the world’s largest education and research organizations. Established in 1994, CERNET now supports more than 2,000 educational facilities in China, including universities, and elementary and middle schools; and more than 20 million users in over 1,600 higher education and research institutions. Internationally, CERNET enjoys high-speed interconnections with academic networks in the U.S., Europe, and the Asia-Pacific region.
From the beginning, CERNET has positioned itself as the primary infrastructure provider for the informatization of China’s education sector. Based on an evolving platform, and using technologies that continue to develop rapidly, the nearly 2,000 colleges and universities across the country communicate with each other to explore how to best conduct educational experiments and openly share data with each other.
Through CERNET, not only is it possible to access all the network-connected schools in China, but the platform also supports access to eduroam, the secure, world-wide roaming access service developed for the international research and education community. CERNET achieves a ‘1 + 1 > 2’ effect by encouraging people to pool their strengths across institutions to accomplish assignments previously restricted to single campuses.
CERNET plans to cooperate with Huawei in a range of areas to continually improve the digital education platform. For starters, the campus network infrastructure is already closely linked to Huawei. Many schools have not only deployed Huawei’s digital platform hardware, but they have begun working with Huawei at higher levels, such as joint research in network behavior to leverage the multitudes of student and teacher data for better, safer, and more flexible network services.
Focusing on the long-term future, CERNET is cooperating with Huawei to conduct research on technology and application trends for years to come.