Standards Safeguard Smart City Constructions
Enterprise products, solutions & services

In recent years, China has attached great importance to Smart City construction. According to a report delivered at the 19th National Congress of the Communist Party of China (CPC), President Xi Jinping has made significant headway toward establishing ‘network power, digital China, and smart society.’ Smart City construction will help cities implement diversified public services with universal benefits, achieve efficient and Smart City management, build intensive and coordinated infrastructure, develop a converged and innovative industry economy, establish secure and controllable protection systems, and further fulfill the strategic goals of a smart society.
Standards are important for the healthy development of Smart Cities in China, and serve as the basis for promoting the convergence, sharing, and development of information resources. In addition, standards are necessary conditions for promoting large-scale applications of intelligent technologies such as cloud computing, the Internet of Things (IoT), and Big Data. In fact, standards are an important guarantee for the quality of China’s new city constructions.
Huawei has been seeking out and joining international industry standards organizations. By adhering to the ‘platform + ecosystem’ strategy, Huawei has cooperated with partners to initiate and promote the development of standards for Smart City architectures with the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), and have built a Smart City ecosystem based on the specifications of the Industrial Internet Consortium (IIC). Based on its evaluation of new types of Smart Cities in China and participation in global standards organizations, Huawei has built a Smart City industry ecosystem that effectively supports the healthy development of Smart Cities around the world.
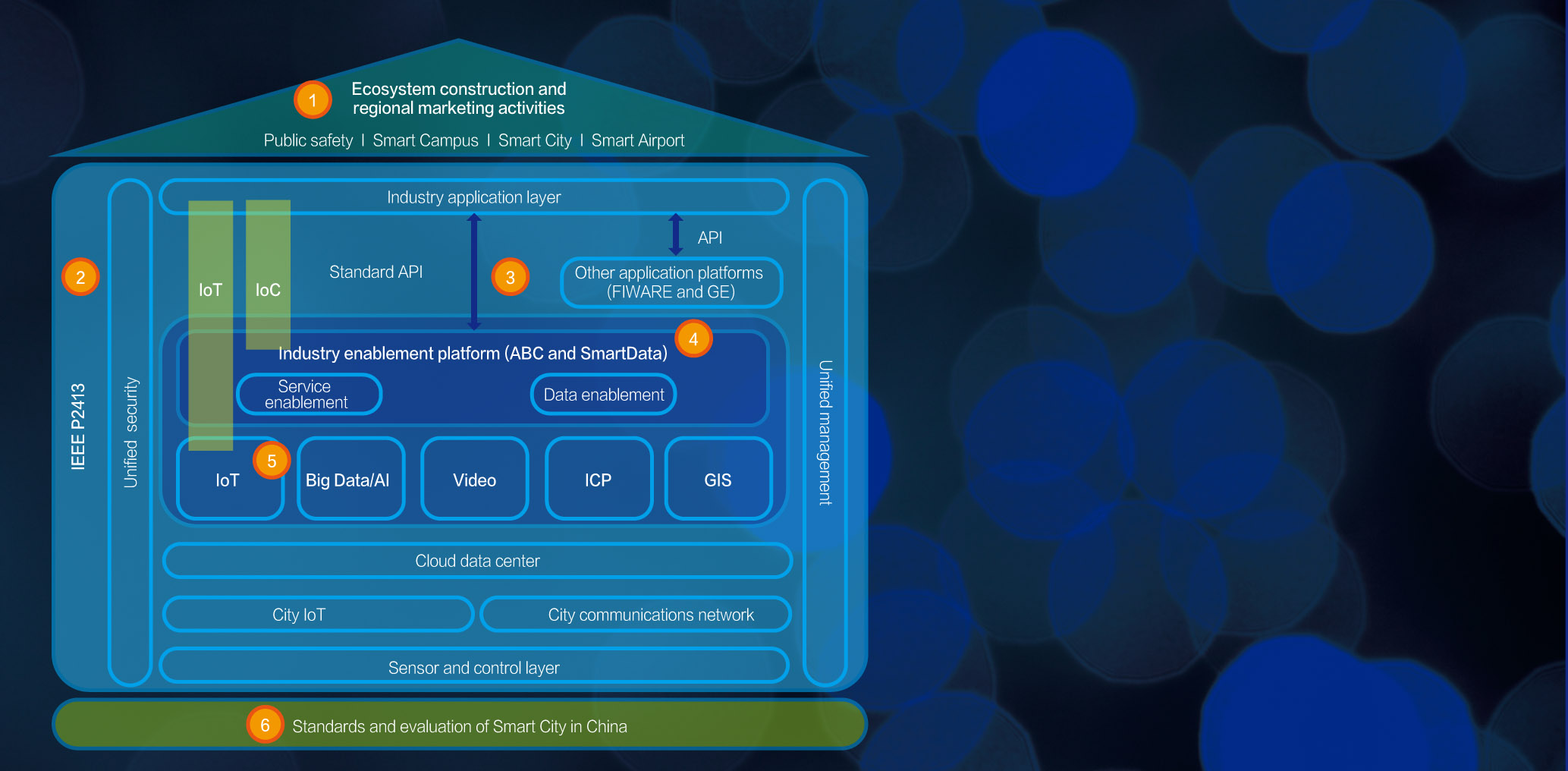
Huawei has actively participated in the formulation of IEEE P2413 (the architectural framework standard of the IoT). Huawei has hosted IEEE P2413 international conferences multiple times, and was elected as an IEEE P2413 editor.
In November 2017, Huawei held the IEEE P2413 working group meeting in Shenzhen, where we introduced the ‘one cloud, two networks, three platforms’ solution architecture and an abstract architecture of four layers (equipment, communications network, IoT platform, and applications) for the Smart City IoT domain. Huawei also defined the IoT platform and specified modules such as device management, connection management, applications, and Big Data analytics. In addition, Huawei successfully added the city Intelligent Operation Center (IOC) solution to the IoT architectural framework standard of IEEE P2413. At the IEEE-Standards Association (IEEE-SA) Corporate Advisory Group (CAG) 2018 meeting in Shenzhen, all CAG members unanimously approved the Huawei-proposed Smart City reference architecture standard project P2413.1, which was a huge milestone for IEEE standards in the Smart City area.
The P2413.1 standard for smart city reference architecture will include Smart City IOC, IoT, descriptions of different vertical applications, and the commonality among them. The architecture will describe the Smart City cloud infrastructure, the edge computing and Big Data analytics technologies, and unified security and management. Smart City applications are rich — including smart water management, smart waste management, smart street lamps, smart parking, smart environmental protection, smart campuses, smart buildings, smart healthcare, and smart government — and the P2413.1 standard will provide a blueprint for cross-domain interworking in Smart Cities.
“Promoting standards and building an ecosystem are the best proof of the importance of P2413 standards,” IEEE P2413 Working Group Chair Oleg Logvinov said. “Development of Smart Cities, as well as edge computing and its relevant enabling technologies, is not possible without the IoT. Huawei is one of the founding members of the IEEE P2413, and Huawei’s Smart City proposal has significantly promoted the current standard development process. It is worth mentioning that Huawei has been the chief editor of the P2413 standard, and Huawei’s leadership in P2413 has continued to improve.”

IIC is an important industry ecosystem. Its mission is to collaborate with all parties in the ecosystem and use common frameworks, interoperation, and open standards to connect and integrate devices, processes, and data. It aims to accelerate the development of the industrial Internet through pioneering business results. The alliance has gathered organizations in related industries to identify, integrate, and promote the best technologies and solutions; advance the development of the industrial Internet industry; and accelerate digital transformation.
In the Smart City field, IIC members have established a series of testbeds to explore new technologies and applications that include smart water affairs, intelligent construction, energy conservation, traffic optimization, and emergency response. They have adopted the IoT, networks, and Big Data, as well as cloud platform technologies for agile transportation, energy conservation, environmental protection, water management, and efficient and safe operations. In addition, a Smart City test bed project has been launched to promote the research and deployment of new technologies and applications in the Smart City field.
More than a core member of IIC, Huawei is a member of the organization’s steering committee, and plays an active role in promoting network technology applications and collaboration between international standards organizations.
For example, Huawei actively promotes LTE-based application solutions in metro and urban rail. Huawei and its partners have created a testbed in IIC to replace the existing Wi-Fi-based train-to-ground communication network with one that can handle multiple services. This network solution, based on the open standard LTE protocol, can greatly improve security and reliability, which reduces O&M workload and costs.
To comply with State Council policy and Smart City construction and city management authority requirements, the Standardization Management Committee of China has established the general team, coordination and promotion team, and expert consultation team for national Smart City standards development. The purpose is to specify the overall framework of China’s Smart City standards and evaluation indicator systems, determine the overall layout and key areas, and assign tasks for key standards development. The teams are attempting to promote the adaptation of China’s standards to meet international standards, and even guide the formulation of new global Smart City standards.
As a key member of both the general and expert consulting teams, Huawei has participated in the organization’s activities and has initiated the formulation of Smart City standards for multiple projects. Huawei has supported the general team in standards interpretation, verification, training, and promotion — and most importantly, promoted the implementation of standards in Smart City construction projects.
Through those efforts, Huawei has established itself as an important contributor to and practitioner of Smart City standards. During its deep engagement in the drafting of China’s Smart Cities Standard System and Evaluation Indicators for New-type Smart Cities, Huawei analyzed Smart City construction requirements, visualized Smart City solution panoramas, and provided references for Smart City construction. Huawei gained in-depth insights into customer business requirements using Smart City panorama and indicator systems, and combined standard implementation with Smart City planning to guarantee the healthy development of Smart City construction.
The Smart City Top-Level Design Guide is one of the most important standards in the system. Smart City requires cross-system interaction, so Huawei needs to consider cross-domain coordination before project initiation. This requires an overall design (covering objectives, key points, and implementation approaches) from a strategic height and a global perspective of city development. As the primary editor of the national Smart City Top-Level Design Guide, Huawei has vigorously orchestrated the top-level design of Smart Cities, proactively assisted in formulating national standards based on practices, and provided top-level design for Smart City construction in more than 60 cities, including Beijing, Shanghai, Shenzhen, Nanchang, Lanzhou, and Sanya.
Additionally, Huawei has actively participated in the verification of China’s new-type Smart City evaluation indicators, which will help guide pilot site construction and future development. In this process, Huawei has integrated its Smart City construction experience and specific project achievements to form an evaluation indicator system that will verify feasibility and promote indicators throughout the entire country.
For example, at the beginning of Smart City construction in Longgang, Shenzhen, Huawei developed a portrait of the city based on the Evaluation Indicators for New-type Smart Cities, and determined the city’s three major pain points: 1) A weak data-sharing foundation caused by information silos; 2) City-governance risks due to large floating populations; and 3) A low sense of personal gain due to unbalanced education, medical care, and government services.
To address those pain points, Huawei formulated a top-level design with the ‘5+6+11’ architecture; built the ‘one cloud, one network, one map, and one device’ unified IT infrastructure; and streamlined more than 50 departments and more than 200 information systems for data aggregation and sharing. In addition, Huawei conducted the development of 11 beneficial services — including government services, smart healthcare, smart education, safe city, and comprehensive governance that improved lives and streamlined city management.

Smart City construction has a long way to go, and standards are an important guarantee and theoretical basis to prevent detours in the process. Authorities, cities, research institutes, and enterprises must make concerted efforts and learn from international standards through international exchanges and cooperation. Huawei advocates openness, cooperation, and a win-win philosophy. It aims to provide basic capabilities for the ICT ecosystem of the future smart society, and promote the continuous progression of the industry and society through alliances.
At present, Huawei has built a large-scale, worldwide industry ecosystem. By attracting more partners and cooperating with industry standards organizations, Huawei strives to guide the development of the entire industry. Huawei believes its global industrial layout and project practices will effectively accelerate the promotion and application of China’s Smart City standards worldwide.